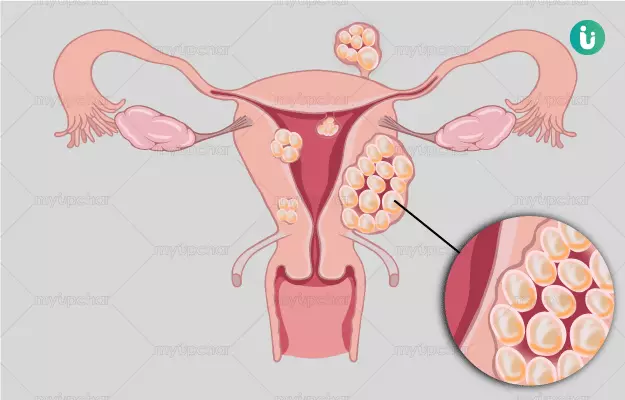
Many women have uterine fibroids at some point in their lives. It is also possible that they have uterine fibroids but they never know about it. This is because uterine fibroids often do not cause any kind of pain or any symptoms. So if you have a uterine fibroid and there are no side effects, how do you know if you have a fibroid or not? And should you be worried about it or not? This article tries to answer these questions of yours.
As women age, they are more likely to have uterine fibroids, especially in the 30s and 40s until menopause. Most women have either mild or no symptoms. But the fibroid can cause pain, bleeding and other problems. Your doctor may detect a lump in the uterus during a gynecological exam or by using imaging tests. It can be treated with surgery or with medicines that slow or stop its growth.
If you don't have any symptoms, you may not even need treatment. Many women with a lump in the uterus can get pregnant naturally. Women who cannot do so may be helped by undergoing infertility treatment.
(Read more -Uterine Fibroids Diet)
This article explains in detail the meaning of lump in the uterus and the symptoms, causes and treatment of lump in the uterus.