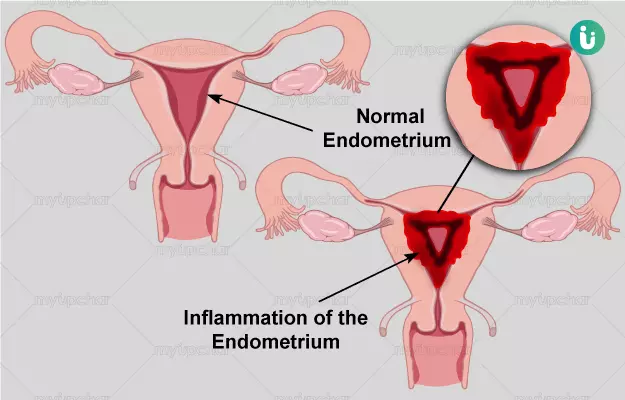
Endometritis is inflammation of the lining of your uterus. This condition usually occurs in a woman after giving birth, but it can also occur in women who are not pregnant. Endometritis are different, however, both conditions affect the lining of the uterus. Another uterus-related condition is called endomyometritis, during which there is inflammation in the inner layer of the uterus, called the myometrium. Endometritis is likely to be short-lived, it is easier to treat than the treatment of endometriosis. This article explains in detail about endometritis i.e. inflammation in the uterus. Which includes the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment and complications of inflammation in the uterus. In this article, we have also clarified the relationship between endometritis and fertility.
(Read more - Metrorrhagia)