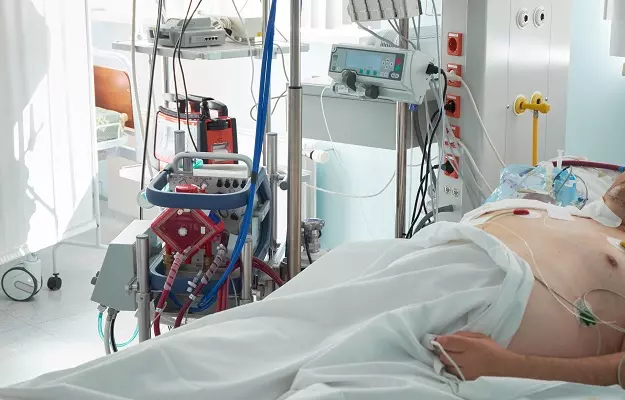
Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, also known as ECMO, is a life support machine. The word "extracorporeal" means outside the body and "membrane oxygenation" means providing oxygen directly to the blood.
ECMO is required for people suffering from a severe and life-threatening illness which obstructs their heart or lungs from working properly. The ECMO machine pumps the blood and adds oxygen to it outside the patient’s body, thus giving rest to the heart and lungs.
When a person is connected to an ECMO, their blood flows through tubing into a machine, which acts as an artificial lung. This machine adds oxygen to the blood and takes out the carbon dioxide from it. Once the blood is oxygenated, it is warmed up to the body temperature and then pumped back into the patient's body.
Patients with severe COVID-19 have also been shown to benefit from ECMO in some cases. In April 2020, the US Food and Drug Administration approved the use of ECMO for COVID-19 patients. COVID-19, or coronavirus disease 2019, is a respiratory tract infection that started a pandemic in 2019, affecting millions of people across the globe.
In this article, we will talk about the uses, functions and the risks related to an ECMO machine.