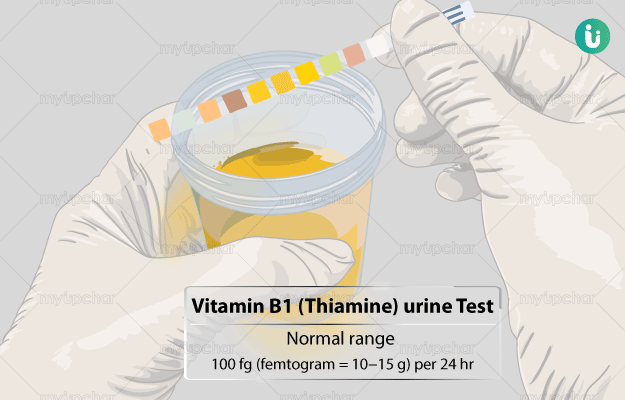
What is Vitamin B1 (Thiamine) Urine test?
The vitamin B1 (thiamine) urine test measures the amount of vitamin B1 in your urine.
Thiamine is a water-soluble vitamin that helps maintain various metabolic functions in the body. It also plays an important role in the growth and development of cells.
vitamin B1 is mostly absorbed through food inside the small intestine and is stored in the liver in small quantities. However, it has a short half-life - it is quickly eliminated along with urine - making it important to replenish it through dietary sources. B1 is naturally obtained from meat (especially pork), fish and whole grains. This vitamin is also present in some fortified foods such as bread and cereals.
Calculating the amount of vitamin B1 in the urine primarily helps to know about the total and needed vitamin B1 intake. Though, it does not give information on the amount of vitamin B1 stored in tissues.