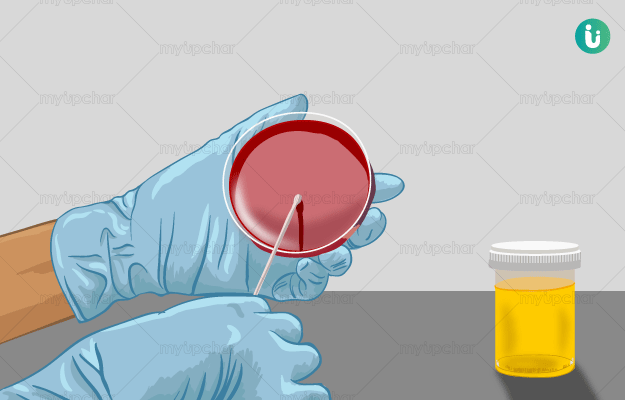
What is urine culture test?
Urine culture test is a laboratory test that checks for microorganisms like bacteria and yeast in urine, the fluid produced by kidneys, which carries waste material and excess water out of the body. The test can detect the presence of a urinary tract infection (UTI) in both children and adults.
In people who have frequent UTIs, other tests like a susceptibility test might be performed with each infection.