What is Calcium Urine test?
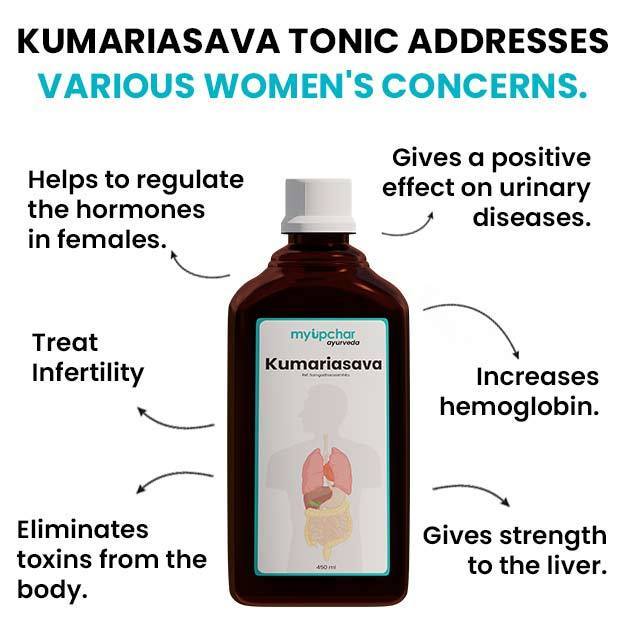
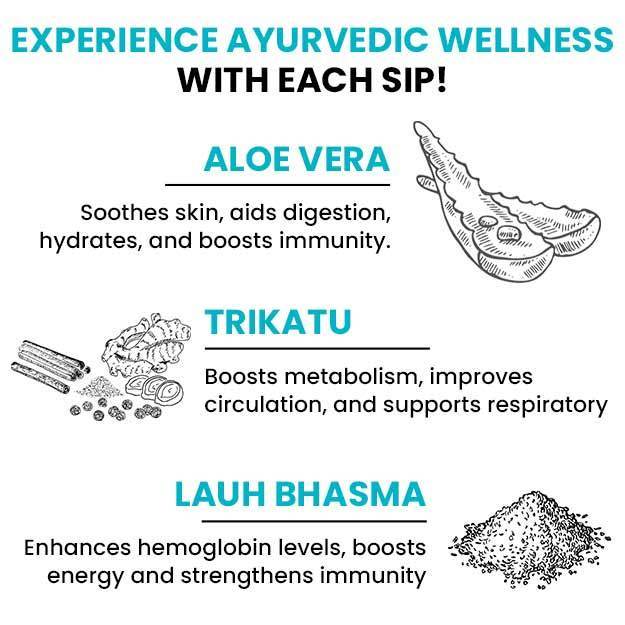
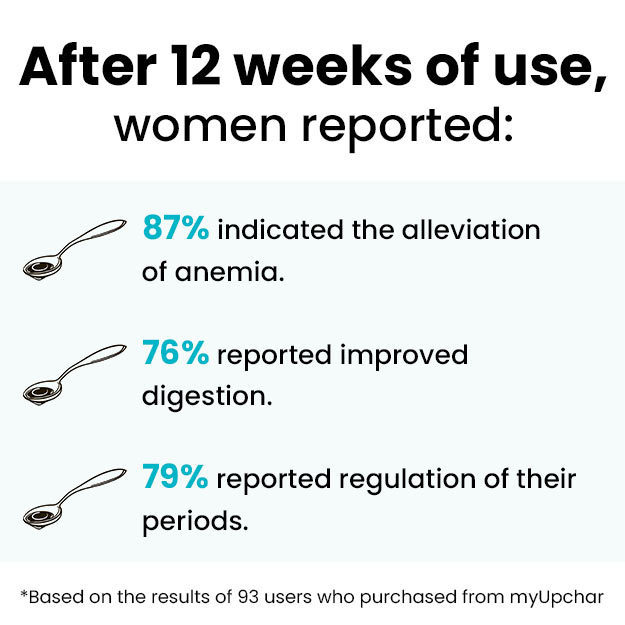
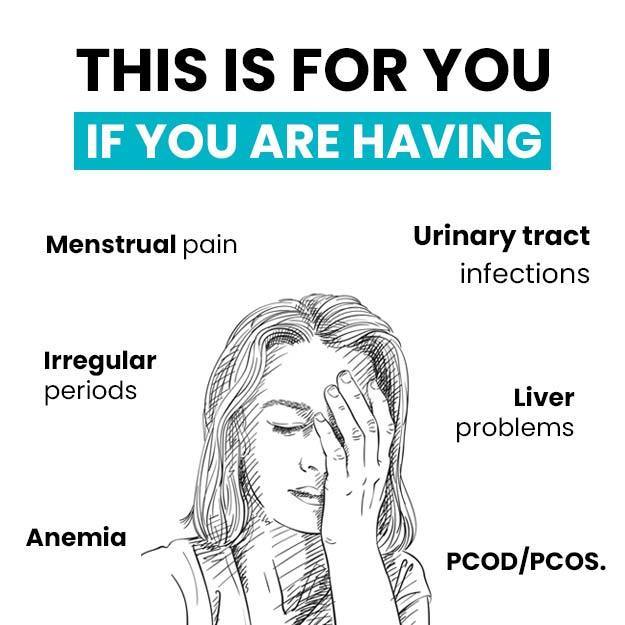
A urine calcium test helps measure the amount of calcium in urine. Calcium is an important mineral that is needed for healthy bones, muscles, teeth and heart. Majority of the total calcium is stored in bones; a minor amount circulates in bloodstream, and the remainder is filtered by kidneys and excreted in urine. When the level of calcium rises in body, the amount of calcium in urine also increases. Excess or very low calcium in blood can indicate a kidney or a bone disorder or other medical conditions. Hence, along with a urine calcium test, other related tests will also be advised to precisely diagnose the cause.