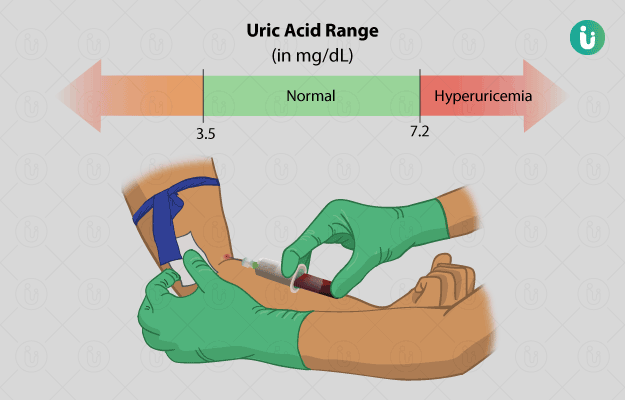
Normal results: A concentration of less than 6 mg/dL in the blood is normal for women and less than 7 mg/dL for men. Normal values for a urine sample may be as follows:
- For a normal diet: 250-750 mg/24 hours.
- For a purine-free diet: <400 mg/24 hours.
- For a high-purine diet: <1000 mg/24 hours.
Normal results for both blood and urine analyses suggest that uric acid is being properly metabolised in the body and kidneys are functioning optimally to excrete uric acid from the body.
Abnormal results: Results indicating excess or less concentration of uric acid in blood and urine indicate the presence of certain health conditions or risk of some disorders. The following conditions may be present if uric acid levels are high:
High uric acid levels in blood also indicate cardiovascular risk. Apart from these conditions, a purine-rich diet containing seafood, red meat, shellfish and liver and some drugs, such as diuretics, niacin and aspirin, may also result in increased levels of uric acid. Uric acid levels that appear lesser than normal, suggest the following conditions:
- Enzyme xanthine oxidase deficiency
- Drugs, such as allopurinol, probenecid and warfarin
- Renal tubular defects
- Liver disease
- Wilson’s disease
- Diet deficient in purines
In conclusion, uric acid is an important endogenous substance in blood, and uric acid test determines its concentration in blood and urine. Abnormally high or low levels indicate a disturbance in metabolism. Regular monitoring of uric acid in blood serum and urine can help diagnose many diseases, and an appropriate correlation can be sought by performing ancillary tests.
Disclaimer: All results must be clinically correlated with the patient’s complaints to make a complete and accurate diagnosis. This information is purely from an educational perspective and is in no way a substitute for medical advice from a qualified doctor.