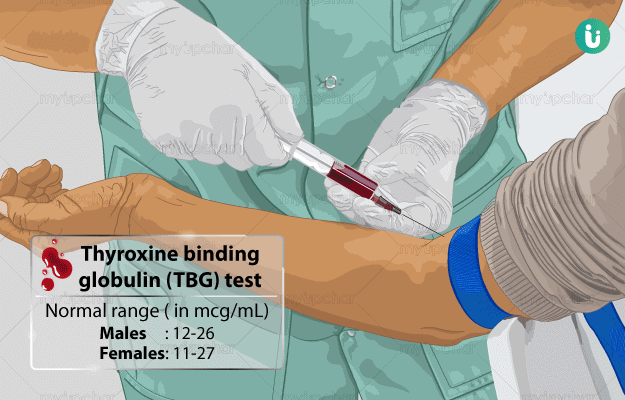
What is Thyroxine Binding Globulin test?
Our thyroid gland produces two hormones – triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4). These hormones are responsible for regulating our weight, growth, internal temperature and energy levels.
Thyroxine-binding globulin is a protein that binds and transports thyroid hormones in the body. Its primary function is to maintain the appropriate level of T3 and T4 in the blood and prevent fluctuations thereof.
A Thyroxine Binding Globulin Test is done to check if you have appropriate levels of this protein in your body.
Changes in the level of thyroid-binding globulin can be caused due to thyroid dysfunction or due to a fluctuation in the level of sex hormones such as oestrogens and androgens.
(Read more: Thyroid function test)