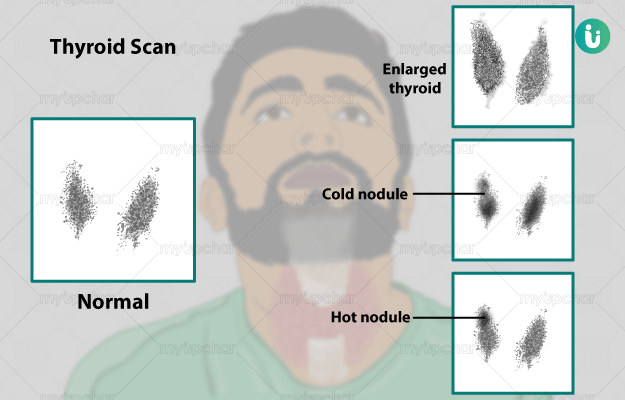
What is a thyroid scan?
A thyroid scan is a test that uses radioactive tracers to observe the function and structure of thyroid gland. The test also shows the shape, location and size of thyroid gland and is typically recommended with a radioactive iodine uptake test for accurate results.