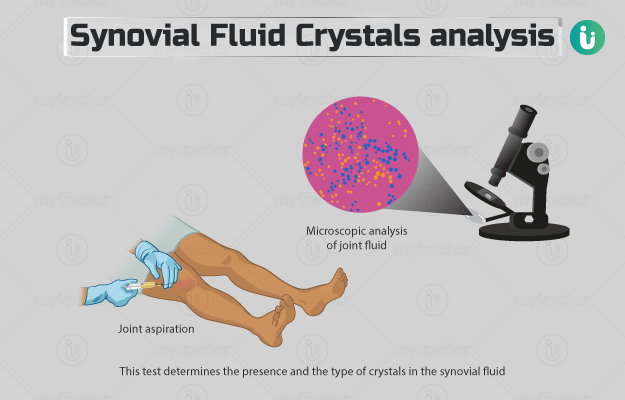
What is Synovial Fluid Crystals Analysis?
This test determines the presence and the type of crystals in the synovial fluid. Synovial fluid is a lubricating liquid present in the spaces within the joints of our body. It has the following functions:
- Provides cushion to the bone ends
- Reduces friction in the joints of knees, hands, feet, shoulders and hips during movement
Different crystals may form in the synovial fluid in different conditions, for example, monosodium urate crystals (uric acid crystals) or calcium pyrophosphate crystals.
A monosodium urate crystal is formed in case of gout. Gout is a painful inflammatory condition, which occurs due to the build-up of uric acid in the body. Uric acid is a waste product of the natural chemical purine. Purine is also obtained from foods, such as shellfish, liver and alcohol. Uric acid is usually eliminated by the body via the urine or stools. However, the level of uric acid can increase due to overproduction by the body, kidney damage, eating too many purine-rich foods or intake of medicines like niacin or aspirin. When the uric acid level rises, it forms crystals and accumulates in the synovial fluid, causing painful swelling of joints. Gout affects men more than women. About 7% of men above the age of 65 are estimated to have gout. (Read more: High uric acid in blood treatment)
Calcium pyrophosphate deposition (CPPD) disease, also known as pseudogout, is a disease caused by calcium pyrophosphate crystal deposits in the joints and soft tissues. It affects about one in every 1000 individuals and is more prevalent among people above the age of 65.
Since there is a close resemblance between CPPD disease and gout, analysis of the synovial fluid crystals helps to diagnose the type of inflammatory joint disease.
(Read more: Synovial fluid analysis)