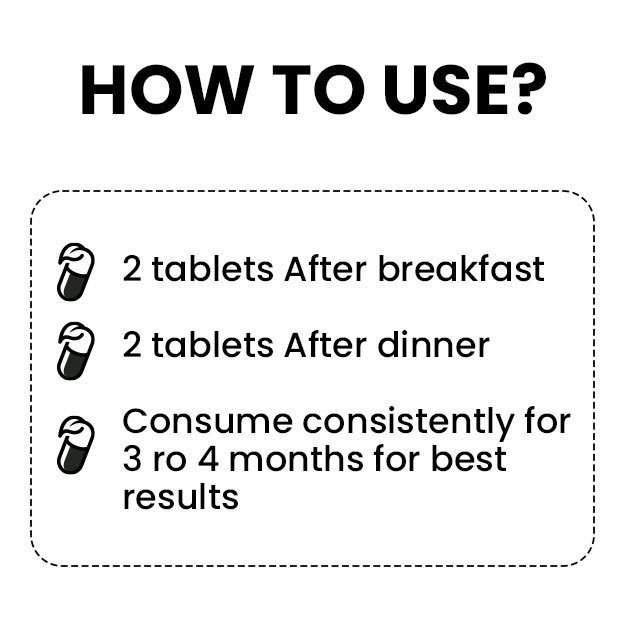
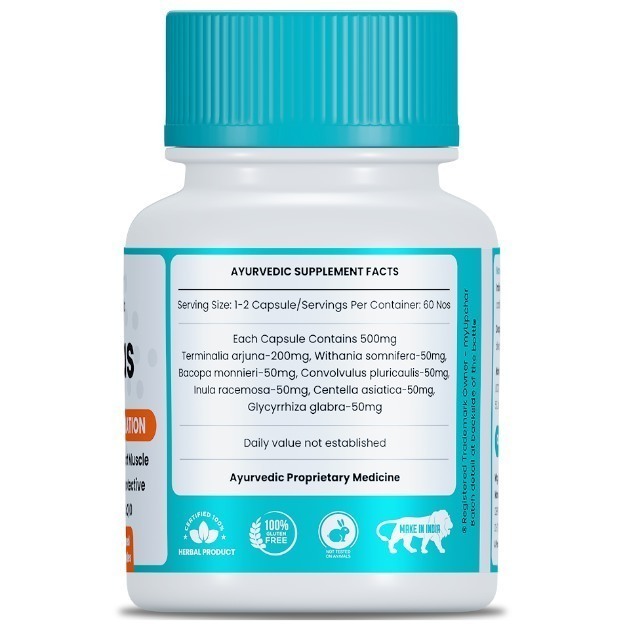
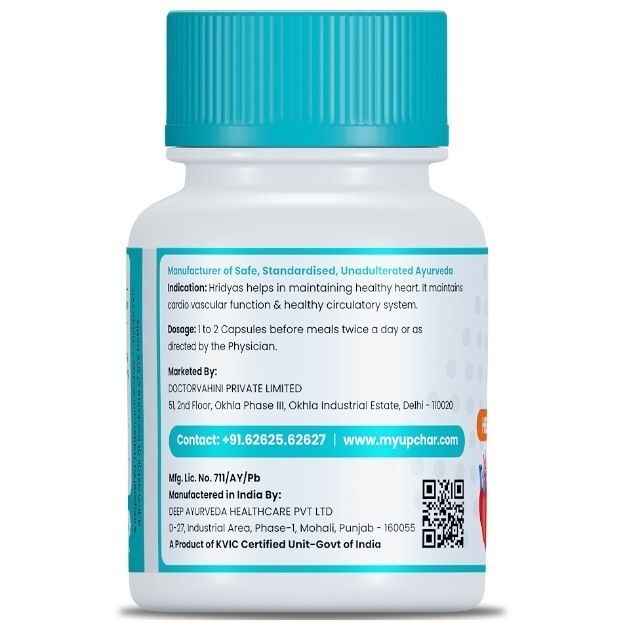
What is a Stress test?
A stress test, also known as the treadmill test, is a non-invasive test that helps in evaluating the heart’s function under physical stress.
In easy words, as an individual walks, exercises or works harder, the heart needs to pump more amount of blood. A stress test determines how much workload your heart can take in such conditions. If there are any issues with blood supply to the heart, ie, with the carotid arteries, it can, in turn, affect the functioning of heart and appear as abnormal results in a stress test.
In a stress test, an individual is asked to walk on a treadmill, until their heart works progressively harder, meanwhile, an electrocardiogram (ECG) is monitored. When the test is in progress, blood pressure is evaluated sequentially, and symptoms, such as fatigue or chest comfort are looked for. Abnormalities in ECG, blood pressure or pulse rate or the presence of chest discomfort indicates that blood flow to the heart is reduced and coronary arteries may have a deposition of plaques.