What is a beta hCG test?
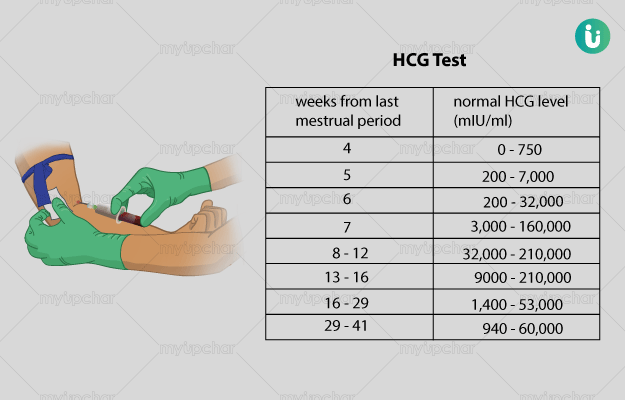
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) is a proteinaceous hormone produced by the body of a woman after she conceives. It helps to maintain pregnancy until the development of placenta and is mainly secreted in the first trimester. The levels of hCG in blood increase from the 8th day after conceiving and peak during the 10th week. hCG test is, therefore, used in simple home pregnancy kits that indicate conception by a colour change of a band in the test kit.
Beta hCG (β-hCG) is a subunit of hCG which can be present in its free form in the serum (the liquid portion of blood). Most laboratories check β-hCG values when the doctor orders an hCG test. Furthermore, the levels of this hormone have been found to be elevated in certain kinds of cancers; therefore, it is also used as a tumour marker.
β-hCG levels in blood are actively being researched as a tool for managing problems associated with in-vitro fertilisation.