Before the actual procedure is done, your doctor will ask you about the location of the lump and when did you first become aware of it. He/she will also inquire whether the lump feels painful or heavy.
Next, he/she will check for the lump manually to understand its location or dimension. Thereafter, the actual procedure is performed.
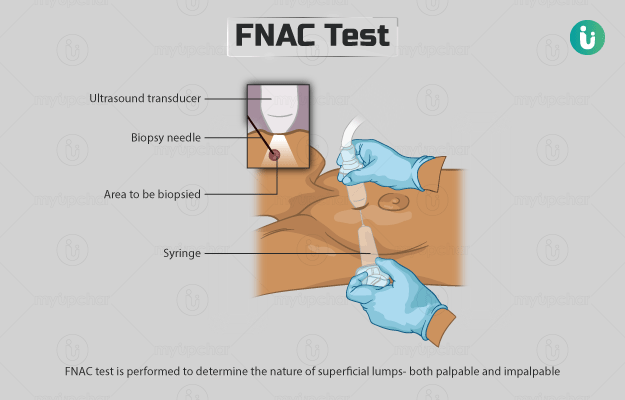
The skin where the test needs to be performed will first be sanitised with an antiseptic solution. If the lump is palpable, your doctor will press over the area gently to identify the spot through which the needle needs to be inserted. If, however, the lump cannot be felt, an ultrasound will be done to locate the area for needle insertion.
Once the lump is identified, your doctor will firmly hold it with one hand, and insert the needle with gentle pressure to withdraw the sample.
Usually, 2-3 samples are required to make a diagnosis. Hence, the lump that needs to be tested is fixed between the fingers as the sample is drawn.
The entire procedure (of inserting the needle and getting the sample) does not take more than 20-40 seconds. The needle will be taken out gently before blood is observed in it. The collected sample will be sent to a laboratory for analysis, and the results should be available in 3-4 days.
This test has no complications when performed by an experienced and skilled practitioner. The only thing one might notice is slight bruising or short-lived tenderness in the area.
Mild pain may be experienced while sample collection, though, the use of a local anaesthetic reduces the discomfort.