Results of the ESR test measure the amount of clear fluid (called plasma) at the top of the test tube after an hour of sedimentation. ESR is represented as millimetre per hour.
Normal results:
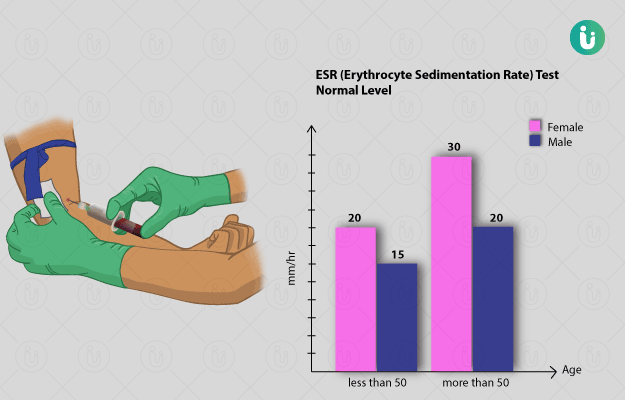
Normal values of ESR are:
- 0 to 10 mm/h in children
- 0 to 15 mm/h in men younger than 50 years
- 0 to 20 mm/h in men older than 50 years and women younger than 50 years
- 0 to 30 mm/h in women older than 50 years of age
Abnormal results:
An ESR value that is higher than normal indicates the presence of inflammatory conditions. Some of the common causes of moderately elevated ESR include:
- Infection
- Anaemia
- Pregnancy
- Ageing
- Kidney disease
- Multiple myeloma
Elevated ESR value can also be due to autoimmune disorders such as:
A lower than normal ESR value indicates the presence of blood disorders such as:
- Sickle cell anaemia
- Leukocytosis, increased white blood cell count that is higher than normal
- Polycythemia
The interpretation of the test results varies depending on parameters like age, gender, the method used to perform the test and medical history of the individual. Moderately elevated ESR values do not confirm the presence of inflammation as they may occur due to factors such as pregnancy.
Some medications may alter ESR values, and your doctor should be informed about the use of such medications. Medicines like aspirin, oral contraceptives, methyldopa, dextran, theophylline, penicillamine, procainamide, cortisone, and vitamin A can increase ESR, whereas quinine, aspirin and steroids may decrease ESR.
Sometimes a repeat ESR is recommended with a time gap between the tests. This is done to monitor disease progression and the effect of treatment. An upward trend in ESR indicates increasing inflammation or inadequate response to treatment.
ESR is not a diagnostic test but indicates the presence of an inflammatory condition in the body. In the case of abnormal ESR values, the doctor will recommend other laboratory tests to identify the cause of inflammation.
Disclaimer: All results must be clinically correlated with the patient’s complaints to make a complete and accurate diagnosis. This information is purely from an educational point of view and is in no way a substitute for medical advice by a qualified doctor.