What is Enteroscopy?
Enteroscopy is a procedure that helps your healthcare provider to examine your small intestine. It is used to:
- Identify or treat the source of bleeding in your gut
- Take a tissue sample (biopsy) from the digestive system for laboratory examination
- Remove foreign objects or small bowel polyps (abnormal growths of tissue)
- Widen a narrowed part (stricture) of the digestive tract
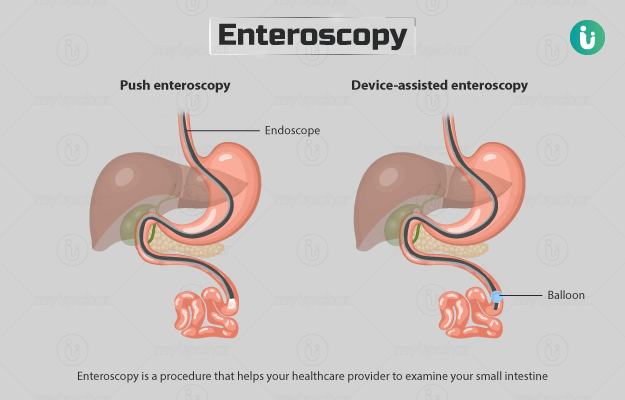
This procedure is performed either by using capsule endoscopy or flexible enteroscopy. For capsule endoscopy, you would have to swallow a tiny capsule containing a camera. Although capsule endoscopy is a safe method to examine the small intestine, it does not allow to obtain tissue samples or carry out treatments. Flexible enteroscopy involves two methods:
- Push enteroscopy: In this method, an endoscope (a long, thin, flexible tube fitted with a camera and light source) is introduced into the gut through the mouth. It goes down into the small intestine till the point where it cannot go further due to sharp bending of the intestine.
- Device-assisted enteroscopy: This procedure also involves the insertion of an endoscope into your digestive tract. The only difference is that the endoscope has a tube over it that uses a corkscrew (spiral) or balloons (single balloon, double-balloon) to assist in insertion. However, the use of overtubes is limited due to discomfort and side effects. Device-assisted enteroscopy can be performed via the anus or the mouth.