What is an Electrocardiography test?
Heart is a vital organ of the body, which is located in the chest cavity, between lungs, in a space behind the breastbone. The heart constantly contracts and relaxes to so as to supply fresh oxygenated blood to various parts of the body. During this process, the heart creates electrical signals, which can be measured to check for any abnormality in heart functioning or the presence of heart diseases.
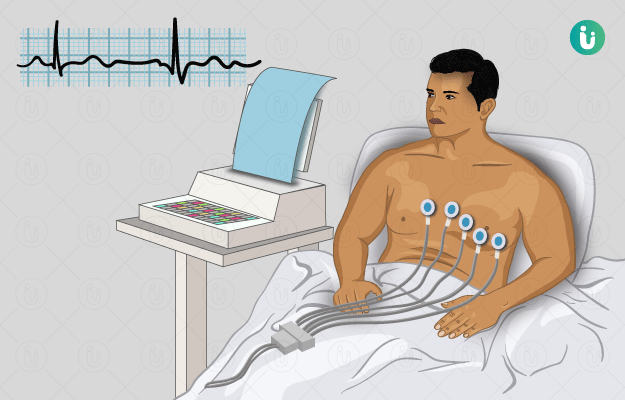
Electrocardiography is a simple and painless procedure that records electrical signals of the heart while at rest and provides results in the form of an electrocardiogram (ECG/EKG). Occasionally, an ECG is recorded while exercising or performing some activity, which is known as ‘stress testing’.
Electrocardiography is an office- or clinic-based procedure and does not require extensive preparation. It is very commonly used by physicians in clinical practice for the diagnosis of some specific heart diseases. It provides information about the heart rate, rhythm, and whether the heartbeat is regular or irregular. Size and position of heart chambers can also be determined using an ECG.