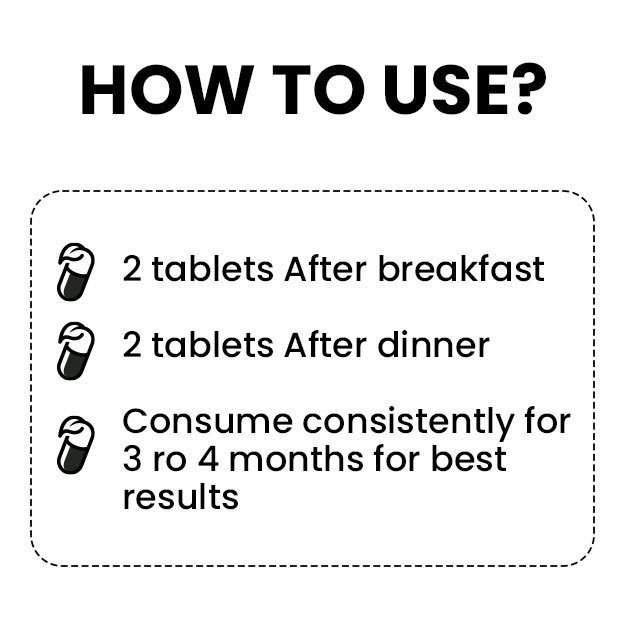
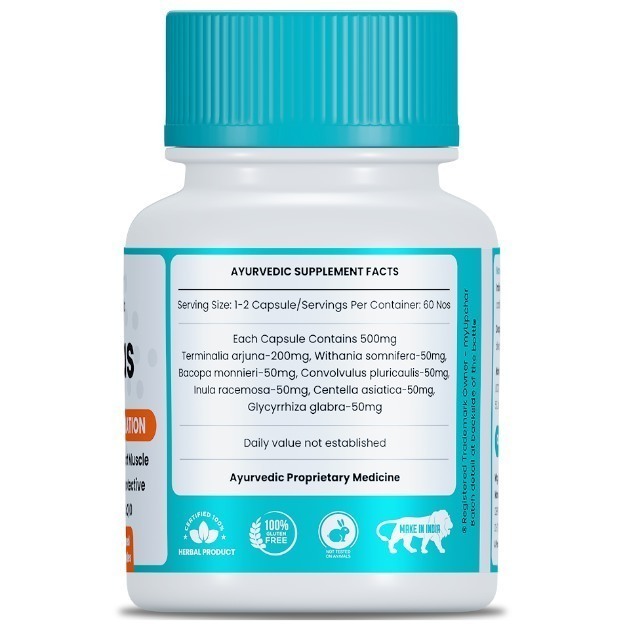
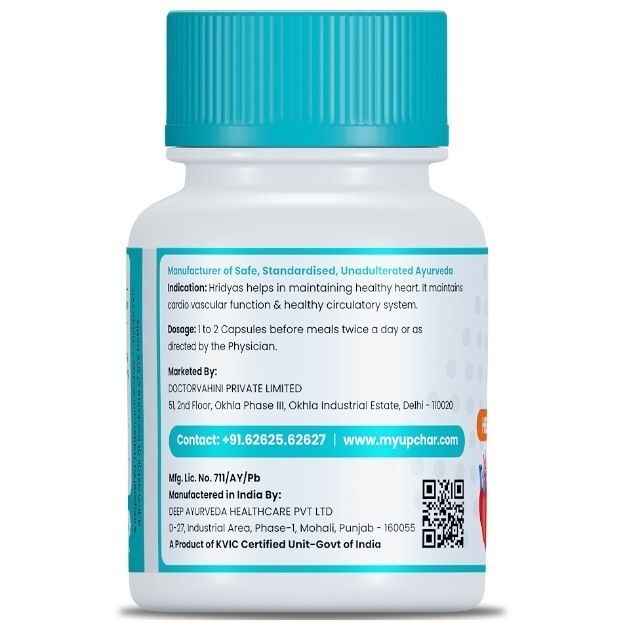
What is Digoxin test?
Digoxin is a drug that is used in the treatment of heart failure (congestive heart failure) and abnormalities in the heartbeat (arrhythmia). It decreases the rate of heartbeat, increases the force of contraction of heart muscles and delays the passage of electric impulse in the heart that causes contraction of the heart.
A digoxin test is a blood test that measures the levels of digoxin and its breakdown products (metabolites) in the bloodstream. Since excess digoxin can be harmful to the body, this test is done at repeated intervals after the administration of this drug to monitor drug dose and avoid its toxic effects in those suffering from heart failure and arrhythmia.