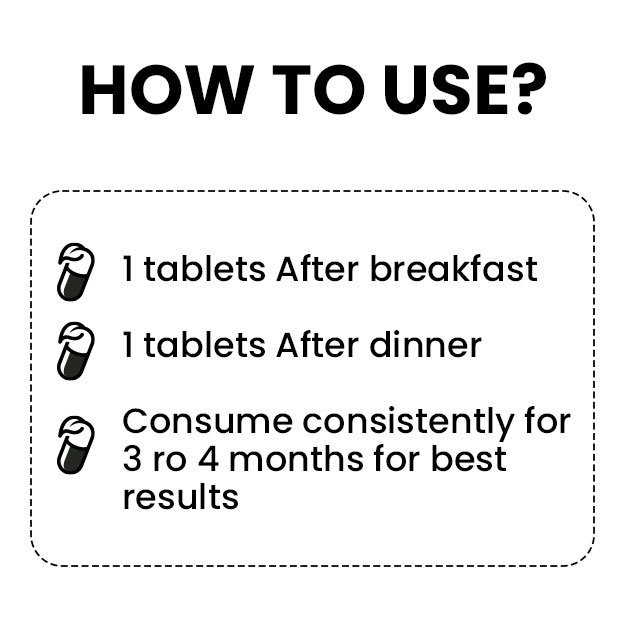
What is Differential Leucocyte Count (DLC)?
Differential leucocyte count (DLC), also referred to as the blood differential test checks for the percentage of different types of white blood cells (WBCs) in the blood. WBCs are immune system cells that are responsible for protecting you from infections, allergies and diseases. There are six different types of WBCs:
- Basophils
- Eosinophils
- Neutrophils
- Band (young neutrophils)
- Monocytes
- Lymphocytes
Each type of WBC has a unique function and hence changes in their levels may indicate specific health conditions. For example., raised eosinophils are usually an indication of allergies.
A DLC test is done to assess these changes in WBCs to diagnose underlying conditions.