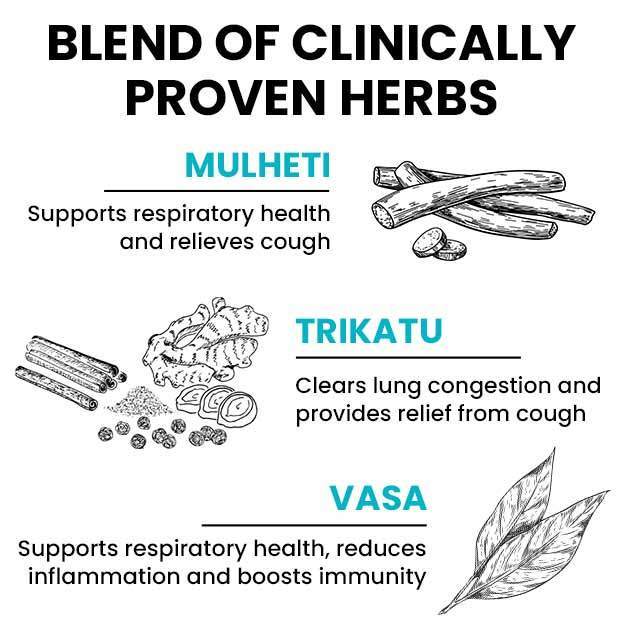
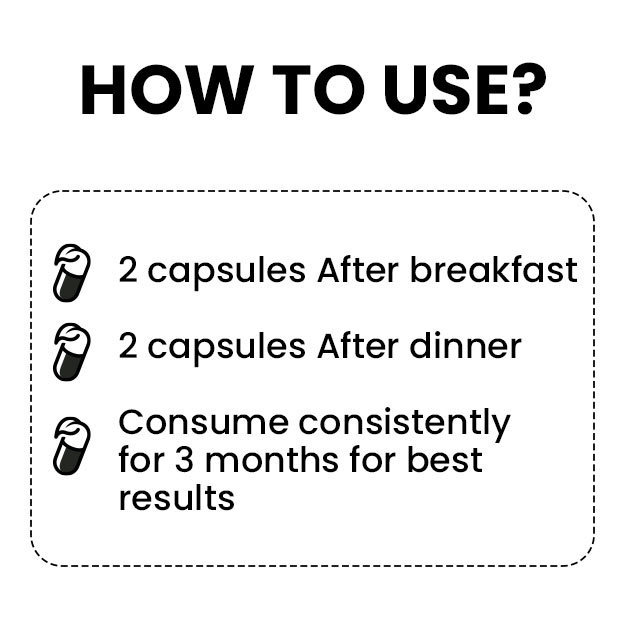
What is a C-reactive Protein (CRP) test?
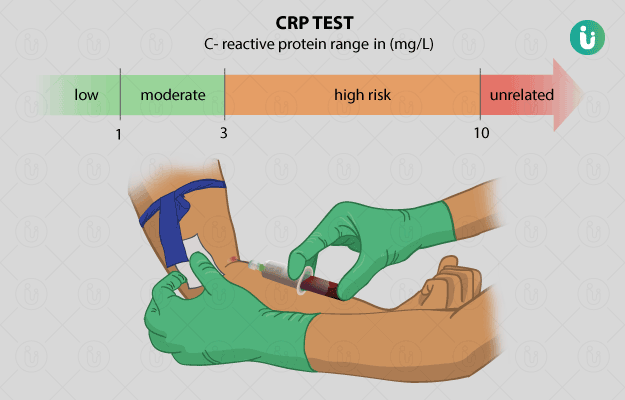
A CRP test is an analytical technique used in laboratories to determine the concentration of C-reactive protein in blood. For this test, blood samples are subjected to techniques, such as nephelometry and turbidometry. CRP is synthesised by hepatocytes in liver. The synthesis of this protein increases several folds during inflammatory diseases, bacterial and viral infections and cardiovascular diseases. There are two types of CRP assays:
- A wide-range assay performed in case of acute infections and inflammatory diseases
- A high-sensitive CRP assay for cardiovascular diseases, also known as hs-CRP or cardio-CRP.
hs-CRP is highly sensitive and can determine very low concentrations of this protein in blood. CRP levels rise immediately within hours of inflammation and fall rapidly once the treatment is initiated. CRP test is more significant than erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) test for dignosing inflammatory conditions, as it is not affected by physiological states.