What is a cervical MRI scan?
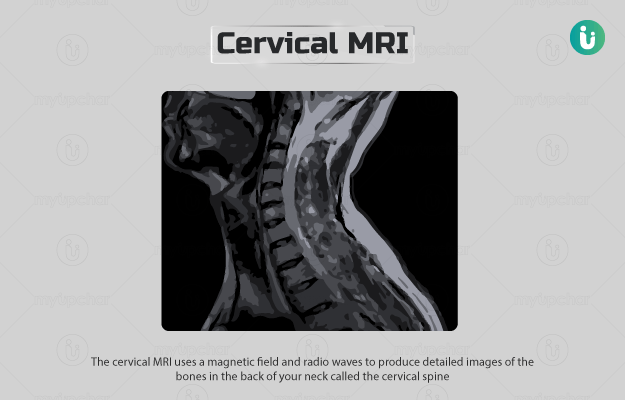
The cervical MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) uses a magnetic field and radio waves to produce detailed images of the bones in the back of your neck called the cervical spine.
During the test, the MRI machine creates a temporary magnetic field in the individual’s body, forcing hydrogen atoms present in the body to align with the field. The transmitter of the machine then sends radio waves that knock the atoms out of alignment. When the radio waves are shut off, the atoms realign and send out distinct signals which are picked up by the receiver of the machine to make detailed images of the scanned area.