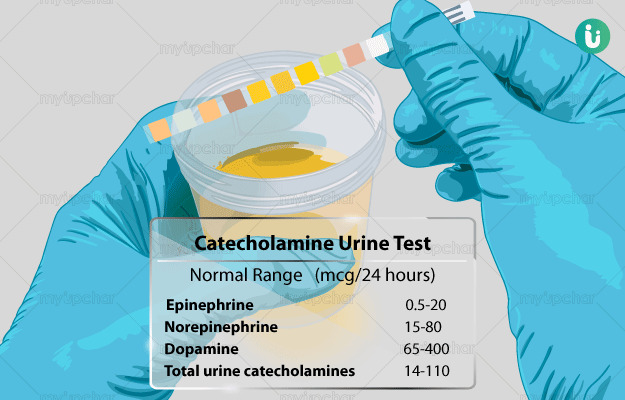
What is a Catecholamine Urine test?
Catecholamines are hormones that are produced by adrenal glands, usually in response to physical or emotional stress. They help the body cope with stress by regulating heartbeat, pulse, blood pressure, blood glucose content and metabolic rate. After completing their action, catecholamines are converted into inactive compounds which are expelled through the urine. This helps maintain the levels of these hormones in the blood.
However, people with adrenal tumours produce large amounts of catecholamines, which shows up in their blood and urine. Excess of these hormones leads to symptoms like hypertension and headaches.
Usually, both a blood and urine test is done to check for catecholamine levels in an individual suspected of adrenal tumours, however, a urine test is more reliable. This is because, in some individuals, the thought of getting a blood test done can evoke anxiety and raise catecholamine levels.
(Read more: Catecholamines blood test)