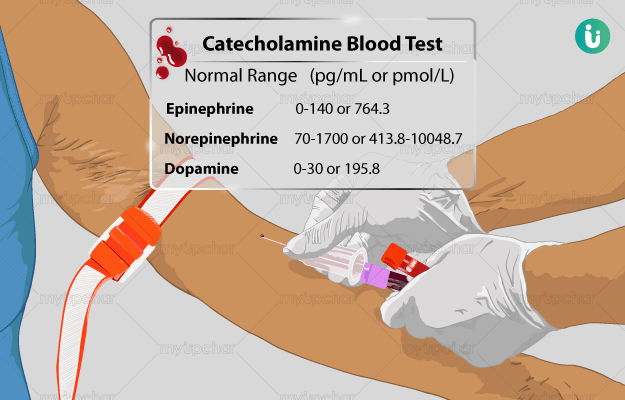
What is a Catecholamine Blood test?
Catecholamines are chemicals secreted in the body by the terminal ends of nerves and adrenal glands - endocrine glands located near the kidneys. They act as hormones and neurotransmitters - chemicals that carry nerve signals. These hormones play an important role in maintaining the internal balance of the body, especially in conditions of stress, illness and other critical situations. There are three types of catecholamines in the body: epinephrine or adrenalin, norepinephrine or noradrenalin and dopamine.
A catecholamine blood test is used to assess the levels of dopamine, epinephrine and norepinephrine in the blood. It is mainly done to check for the presence of adrenal tumours and cancers.