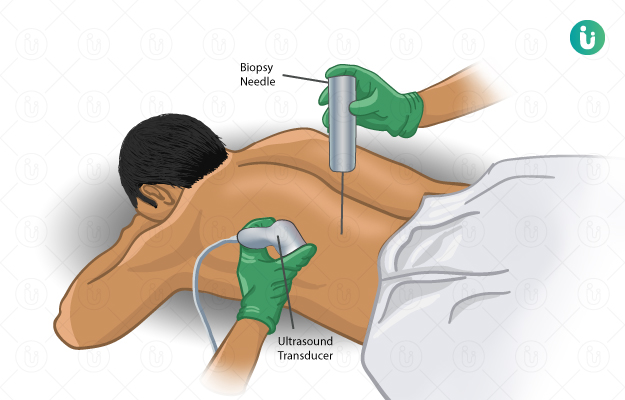
What is a biopsy?
A biopsy is a medical procedure involving the collection and microscopic examination of a small tissue or cell sample from body to analyse it for the presence of any disease or damage. Some other tests may also be performed on this sample to identify the exact cause of symptoms experienced by an individual. A biopsy can be performed on all parts of body, including skin surface, organs and other structures. It can be used for diagnosing many conditions but is most commonly used to detect the presence of cancerous cells.