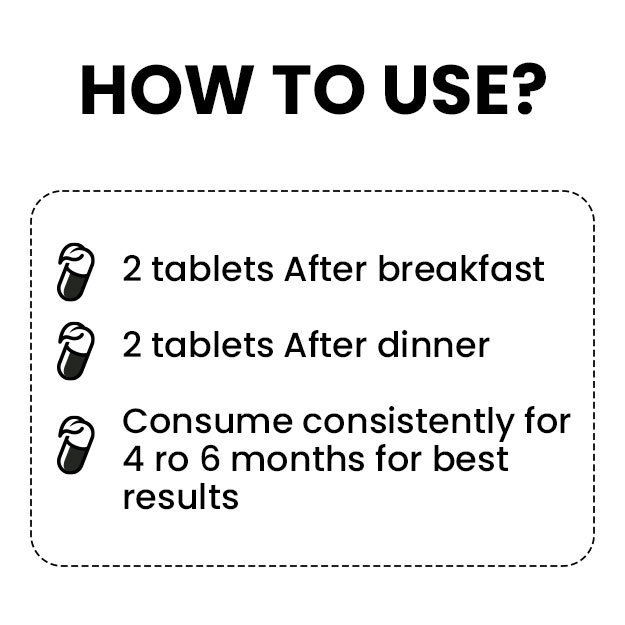
What is Bilirubin test?
A bilirubin test measures the levels of a yellowish substance called bilirubin that is produced by the breakdown of RBCs in body. Bilirubin is also produced in the liver to help digest food. This test is conventionally done as a part of liver function tests and it helps determine how well the liver is functioning.
Bilirubin test helps determine the total bilirubin present in the body consisting of:
- Indirect (Unconjugated) bilirubin: Bilirubin present in blood after RBC lysis. It is bound to albumin protein
- Direct (Conjugated) bilirubin: Bilirubin bound to sugars and formed in liver.
Total and direct bilirubin can be measured in the blood, from which, one can derive indirect bilirubin levels. If one has liver damage or an increased rate of red blood cell destruction, bilirubin can leak into the blood, build up to unhealthy levels and cause skin and eyes to turn yellow; this condition is called jaundice. A healthy liver removes most of the bilirubin through excretion but a small amount remains in blood.
So, bilirubin can be tested in both blood and urine.