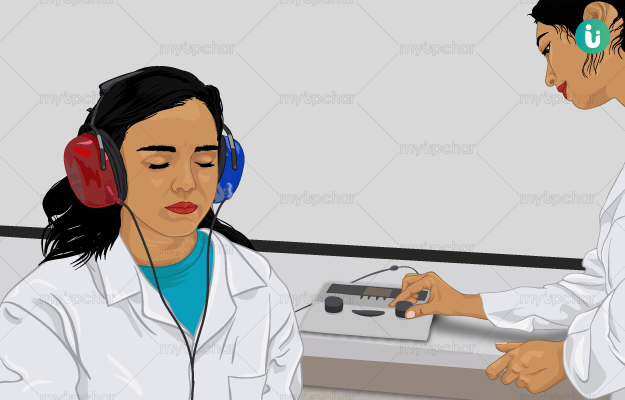
What is an Audiometry test?
Audiometry is a relatively simple test, which is done to test one’s ability to hear sounds. Hearing occurs when sound (in the form of waves) from the environment enters the ear and nerves in the inner ear from transfer it in the form of impulses to the brain for interpretation.
Audiometry tests assess air conduction (when sound waves travel to the inner ear through the ear canal, eardrum and the middle ear) and bone conduction (when sound waves pass through bones around and behind the ear) to check the hearing of an individual.