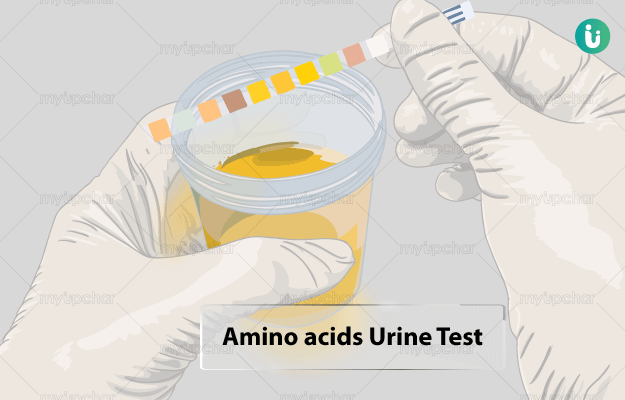
What is Amino Acids Urine test?
Amino acids urine test determines the level of amino acids present in your urine.
Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins which perform several important functions in our body. Our body needs 20 different amino acids for its growth and development. These are broadly classified as essential and non-essential amino acids. Essential amino acids are obtained from dietary sources, whereas non-essential amino acids are produced in the body.
Amino acids are also needed for energy production, synthesis of hormones, neurotransmitters (chemical messengers that carry signals from one nerve cell to the other) and melanin (skin pigment) in the body.
Excess amino acids are converted to urea in liver and expelled through kidneys with urine. Dysfunction in either of these organs or a metabolic error may increase the urine amino acid levels. An amino acid urine test is mainly done to check for abnormalities related to either the metabolism or transport of an amino acid that usually manifest in the form of high urine amino acids.