What is an AFB (Acid-fast Bacilli) Culture test?
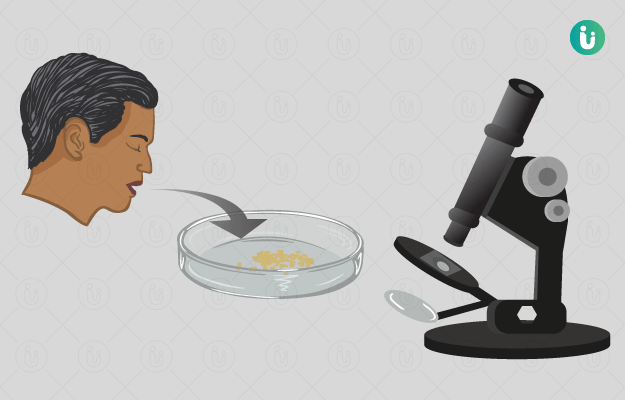
An acid-fast bacilli (AFB) culture test detects AFB that retain the colour of a stain after an acid wash. This test is done to diagnose diseases caused due to Mycobacterium infection such as tuberculosis, leprosy, HIV-related infections, lung, skin and soft tissue diseases. AFB test also helps monitor the efficiency of treatment of these diseases.
A sample of sputum or tissue is obtained from the patient for culture. It is placed in a container with nutrients for the bacilli to grow. A positive bacterial growth over a period of time in the container indicates a positive test and mycobacterial infection.
An AFB smear is usually done before the culture for a presumptive diagnosis. Positive smears signify a possible infection, and culture will confirm the diagnosis. If the smear is negative but clinical suspicion is high, a culture may still show microbial growth that was undetectable through microscopy. AFB cultures also help recognise specific mycobacterium species and identify whether the organism is resistant to antibiotics.