Summary
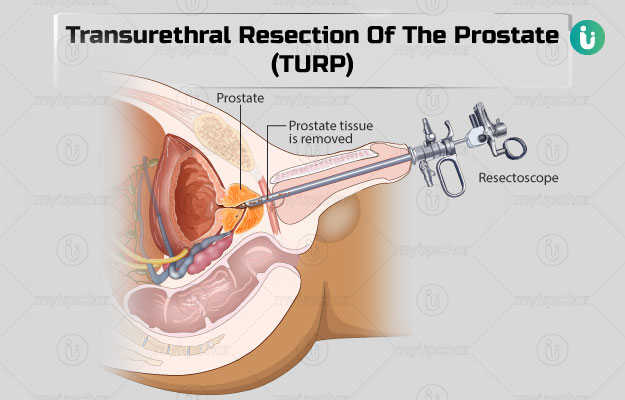
Transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) includes the surgical removal of certain parts of the prostate gland. It is done for the treatment of benign prostate hyperplasia, a condition that causes the enlargement of the prostate gland. The prostate gland resides below the urinary bladder and is coiled around the urethra, which is the tube that vacates urine from the bladder to outside the body. The enlargement of the prostate gland constricts the urethra and restricts the flow of urine, thus resulting in symptoms such as trouble in urination, frequent urination, the inability to empty the bladder and so on. In TURP surgery, the surgeon uses a long, slender instrument called a resectoscope that has an electrical wire loop, to cut the desired parts of the enlarged prostate gland. The surgery may take up to 60-90 minutes for completion. A flexible tube known as a catheter is inserted in the bladder after the surgery for draining out urine and blood. You may need to use the catheter for two to three days until your urine is clear. Depending on your condition, you may have to stay at the hospital for two days or longer. The surgery helps in improving the urine flow and providing relief from the symptoms of benign prostate hyperplasia.