Summary
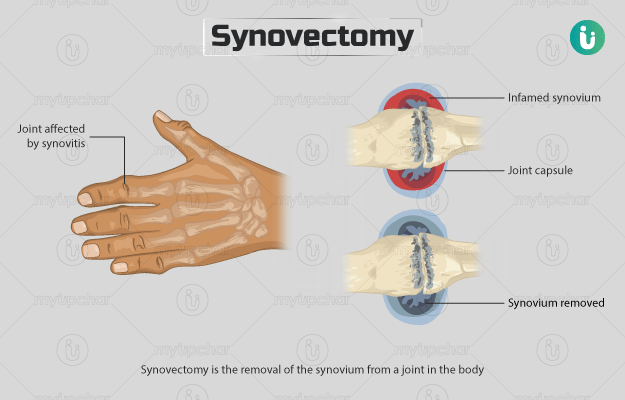
Synovectomy is the removal of the synovium from a joint in the body. Synovium is the inner soft layer of a synovial joint (joint of the knee, shoulder, elbow, hip for example). Owing to heredity, overuse, or injury to the joints, this layer becomes swollen and lead to over-production of synovial fluid (fluid that lubricates synovial joints) within the joint capsule, a condition known as synovitis. Joints affected by synovitis become painful, sore, and stiff, preventing the normal range of movements. Synovectomy is largely indicated in people with inflammatory or rheumatoid arthritis and chronic degenerative joint diseases. The procedure helps relieve the symptoms of the conditions. It can be carried out by open and arthroscopic approaches. However, in individuals or children with haemophilia, radiation synovectomy may be considered.