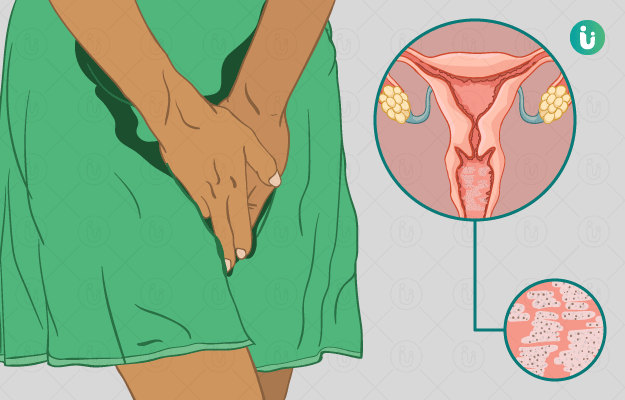
Vaginal yeast infection is a very common infection that affects most of the women at some in their lives. Burning and itching of the vagina and the vulva along with thick white discharge and irritation are the symptoms seen in women with a vaginal yeast infection. Vaginal yeast infection is an overgrowth of a type of fungus called yeast in the vagina. It is also known as vaginal candidiasis. It is not a sexually transmitted infection, but a woman can spread the fungus through the mouth to genital contact.
The treatment of yeast infection depends on the extent of severity of the infection. An uncomplicated infection would have mild to moderate symptoms, whereas a complicated infection would last long and thus would need a long-term course of treatment. Women prefer over the counter medications for self-treatment of these infections. Being sexually active, having uncontrolled diabetes, and use of antibiotics are some of the factors that increase your risk of having a vaginal yeast infection. Discomfort is often the major complication associated with vaginal yeast infections. Symptoms of the infection disappear with proper treatment in most women.

 Doctors for Vaginal Yeast Infection
Doctors for Vaginal Yeast Infection  OTC Medicines for Vaginal Yeast Infection
OTC Medicines for Vaginal Yeast Infection
 Vaginal Yeast Infection articles
Vaginal Yeast Infection articles
 Ayurvedic Treatment of Vaginal Yeast Infection
Ayurvedic Treatment of Vaginal Yeast Infection
 Diet for Vaginal Yeast Infection
Diet for Vaginal Yeast Infection
 Homeopathic Treatment of Vaginal Yeast Infection
Homeopathic Treatment of Vaginal Yeast Infection
































 Editorial Team
Editorial Team

 Dt. Akanksha Mishra
Dt. Akanksha Mishra
 Dr. Rachita Narsaria
Dr. Rachita Narsaria
 Dr. Laxmidutta Shukla
Dr. Laxmidutta Shukla











