What is trigeminal neuralgia?
Trigeminal neuralgia (TN) refers to the sensation of sudden and severe facial pain, which may last from a few seconds to a few minutes. This condition may occur on either one side of the face or both the sides.
What are its main signs and symptoms?
TN is more common in individuals over 50 years of age.
The pain associated with trigeminal neuralgia is mostly described as a sharp, sudden and severe form of pain. It may also be accompanied by a burning sensation.
- The pain may arise suddenly and usually stops abruptly as well.
- The pain may be triggered during daily activities like eating, shaving, washing the face, and brushing the teeth.
- The pain may also affect the individual suddenly while sleeping.
Although, the condition is not fatal, it can make the individual very uncomfortable. The symptoms are progressive in nature which means that the pain attacks may aggravate over time.
What are the main causes?
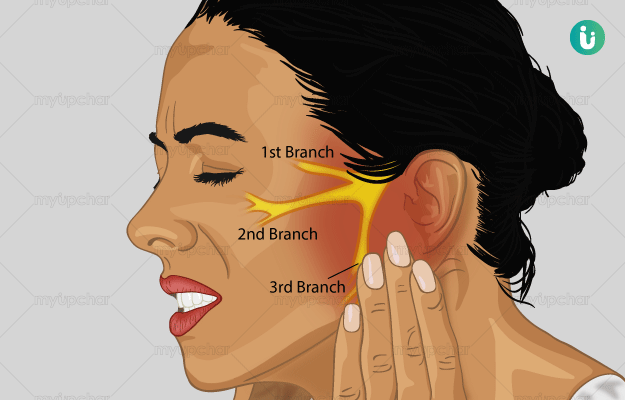
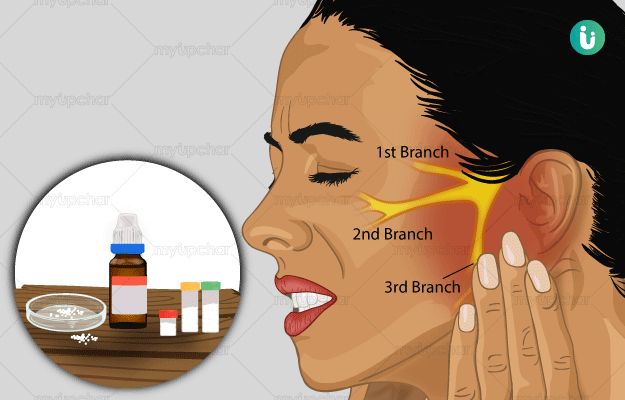
The primary cause of trigeminal neuralgia is the compression of the trigeminal nerve which is present in the skull and is responsible for transmitting the sensation of pain or touch from the face, teeth and mouth to the brain.
This compression may be due to an enlarged adjoining blood vessel. The symptoms of TN may also occur in individuals with multiple sclerosis as this disease causes damage to the trigeminal nerve.
In rare cases, the nerve may be getting compressed due to a nearby tumour along the course of the nerve.
Injury to the trigeminal nerve due to trauma or some medical surgery may also cause TN symptoms.
How is it diagnosed and treated?
Trigeminal neuralgia is diagnosed with the help of a physical and neurological exam. The doctor may also conduct a few scanning tests like skull X-ray, CT scan and MRI in order to eliminate other causes of the facial pain.
The treatment options of TN include anticonvulsant medicines which help in preventing the nerve from getting triggered. In some cases, surgery may be done to relieve the pain.

 Doctors for Trigeminal Neuralgia
Doctors for Trigeminal Neuralgia  OTC Medicines for Trigeminal Neuralgia
OTC Medicines for Trigeminal Neuralgia
 Trigeminal Neuralgia articles
Trigeminal Neuralgia articles

 Homeopathic Treatment of Trigeminal Neuralgia
Homeopathic Treatment of Trigeminal Neuralgia






 Dr. Rachita Narsaria
Dr. Rachita Narsaria











