What is Rotavirus?
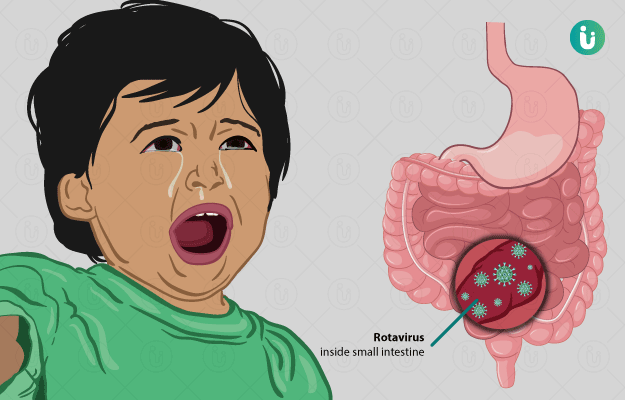
Rotavirus is a contagious virus that infects the digestive tract, resulting in vomiting and diarrhoea. The condition is common in young children and babies. However, it can be prevented by immunisation and attention to personal hygiene. Infection with this virus is one of the commonest reasons for an upset stomach in children.
What are its main associated signs and symptoms?
The symptoms of Rotavirus infection appear in children around two days after the ingestion of contaminated food or water. Symptoms include:
- Fever
- Diarrhoea
- Vomiting
- Abdominal pain
- Loss of appetite
- Dehydration
- Decreased urination
- Dry mouth and throat
- Dizziness
- Fussiness or irritability
Children with a history of the condition may also develop rotavirus as there is no immune protection from the virus. However, the first infection of the virus is more severe.
What are its main causes?
Rotavirus is a communicable disease that spreads through:
- Direct contact with faeces of an infected child.
- Close contact with the infected person.
- Contact with toiletries, bedding and food.
- Not maintaining hygiene.
Since rotavirus is contagious, it spreads quickly through the family, school and other public institutions.
How is it diagnosed and treated?
In its severe form, Rotavirus can lead to dehydration-related complications. The diagnosis is dependent on the detection of the virus in human faeces. The doctor may conduct a stool test to ascertain the condition. Further tests called enzyme immunoassay and reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (PCR) can benefit in diagnosis.
Treatment:
Prevention is better than cure in the case of rotavirus infections. Therefore, avoidance of public places and the maintenance of personal hygiene is recommended. Also, avoid touching the infected bedding and clothes of the patient to safeguard yourself.
Use of oral rehydration solutions like drinking homemade lemonade, buttermilk, coconut water, sugar solution (made with 6 teaspoons of sugar and half a teaspoon of iodized salt in one litre of boiled drinking water) to replenish lost salt and fluids. It is important to avoid all outside food till complete recovery ensues.
The treatment of the rotavirus infection is usually based on the symptoms and the doctor may advise complete bed rest. It is important to keep yourself hydrated and avoid eating uncooked food.
Likewise, two vaccines can be administered to infants to get optimal protection against the virus.
- RotaTeq (RV5) to be given at 2,4 and 6 months.
- Rotarix (RV1) for infants of 2 and 4 months.

 Doctors for Rotavirus
Doctors for Rotavirus  OTC Medicines for Rotavirus
OTC Medicines for Rotavirus
 Rotavirus articles
Rotavirus articles






 Editorial Team
Editorial Team











