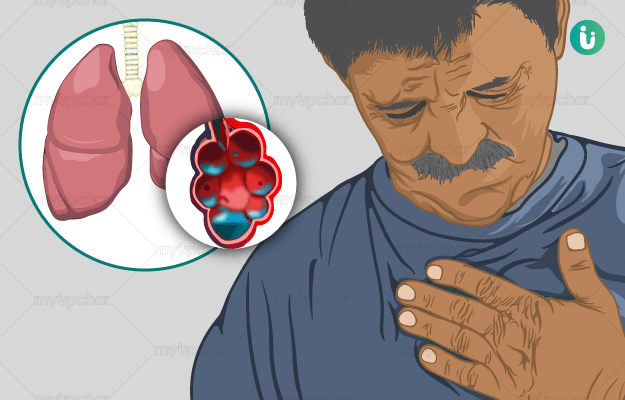
The human respiratory system starts from the nose and mouth, which are attached to the pharynx (throat). The pharynx collects all the air and passes it down to the trachea (windpipe). The windpipe goes down the middle of the upper chest and divides into two bronchi - each of these goes into a lung. These bronchi further divide like the branches of a tree inside the lungs and the divisions are called bronchioles. At the end of each bronchiole, there are small air-filled sacs which are called alveoli. Alveoli are responsible for the exchange of air in the lungs. The alveoli pass the oxygen to the blood and pick up the carbon dioxide to exhale.
Pulmonary edema is the medical term for abnormal fluid collection in the extravascular space (space around the cells) of the lungs. It occurs when the alveoli fill up with excess fluid - this fluid gets leaked out of the blood vessels in the lungs. This creates problems in exchanging oxygen and carbon dioxide, leading to difficulty breathing and low concentration of oxygen in the blood. This condition may occur suddenly (acute) or over a long period of time (chronic pulmonary edema).
The main symptoms of pulmonary edema are swelling of the lower extremities and different types of shortness of breath such as orthopnea, which is difficulty breathing while lying down, and paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea, which is an extreme breathlessness during the night which wakes the patient up from sleep.
Pulmonary edema can occur as a result of heart disease, lung disease, kidney disease and altitude sickness among other things.

 Doctors for Pulmonary Edema
Doctors for Pulmonary Edema