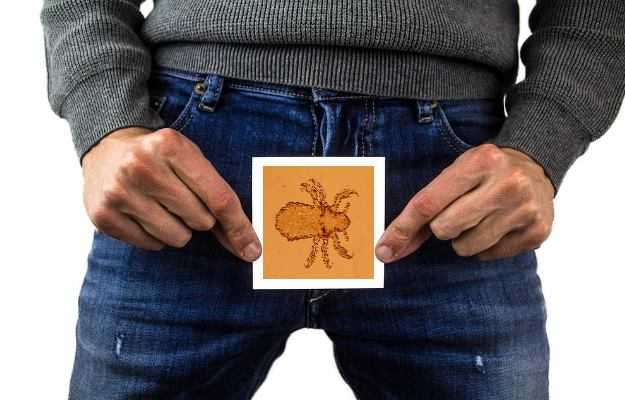
What are pubic lice?
Pubic lice or crabs is a sexually transmitted infection caused due to the crab louse Pthirus pubis. The louse looks like a small, light brown, flat parasite. It sticks to the coarse skin and hair in the genital area causing itching and red spots. Pubic lice feed on human blood and reproduce by laying eggs near hair follicles. Sometimes these lice also spread on other body hair including those of legs, armpits, beard, moustache, eyelashes and eyebrows.
Though it is a common notion that pubic lice spread to due unhygienic conditions, in truth, anybody can get crabs if they get in contact with these parasites.
What are the main signs and symptoms of pubic lice?
Itching and redness in the genital area are two of the most common symptoms of pubic lice. They occur as the body’s reaction against louse bite. Some other symptoms of pubic lice include:
- Intense itching in the genital area at night
- Sores in the genital area
- Apart from this, you can see lice and lice eggs on your genital area
- You may also find minute white debris from lice on your underwear
What are the main causes of pubic lice?
Pubic lice spread through direct skin to skin contact from with an infected person, mostly during sexual intercourse.
Lice or lice eggs can also spread through shared towels and bedsheets and rarely through toilet seats.
The transferred lice settle down the new host and reproduce to increase their population.
How are pubic lice diagnosed and treated?
The diagnosis of pubic lice does not require any equipment or tests. Just a visible identification of Pthirus pubis is enough - a magnifying lens may help. Your doctor may also check for the extent of redness and sores. Presence of lice eggs is not always a confirmatory indicator. Unviable or dead eggs may still be hanging on hair shafts after successful treatment. Once confirmed for having pubic lice, your doctor may recommend the following treatment:
- The main ingredients that can help in treating pubic lice are pyrethrins and piperonyl butoxide. Your doctor may recommend you lotions or other products based on these chemicals
- If the lice have spread to areas like eyebrows or eyelashes, the medications will differ. Soft paraffin may be recommended for such delicate areas. It helps kill the lice by suffocation
- Apart from this, you may be advised to comb your pubic hair with a thin tooth comb to remove the attached eggs
- Mostly the treatment is completed within a week, rarely there is a need for more medication
- However, if the louse doesn’t go in a week, your doctor may recommend you to use other medications like Malathion lotion for some more time
- Since the parasite spreads through sexual contact, partners of crabs patients are generally also diagnosed for pubic lice
- It is recommended to use warm water to wash used clothes along with bedsheets and towels of the infected person. This kills lice and lice eggs that may have been transferred to these items, thus preventing the infection from spreading to other members of the family

 Doctors for Pubic lice
Doctors for Pubic lice