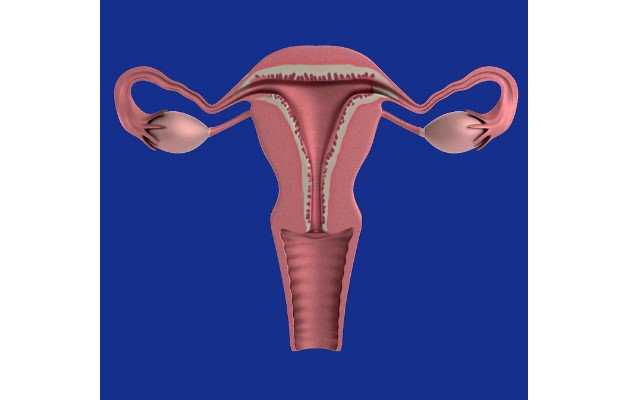
What is primary ovarian insufficiency?
Primary ovarian insufficiency is a condition in women where menopause occurs before the age of 40 along with hormonal imbalance. Otherwise, premature menopause occurs quite rarely.
What are its main signs and symptoms?
Inability to conceive is a major and definitive sign of someone suffering from primary ovarian insufficiency, apart from the other obvious signs and symptoms of the condition, which include:
- Irregular or absent periods.
- Night sweats.
- Decreased sex drive.
- Feeling warm throughout the body, also termed as hot flashes.
- Unexplained irritation and lack of concentration.
- Vaginal atrophy (damage or destruction of the vaginal tissues) due to the thinning of the ovarian walls and pain during sex or conception.
What are the main causes?
Causes of primary ovarian insufficiency can be natural or due to a hormonal imbalance or a genetic disorder. Some of the main causes resulting in the condition are:
- Turner’s syndrome – A condition in which a complete deletion or absence of X chromosome is found in the cells.
- X chromosomal abnormalities – Failure of ovarian functions are associated with any abnormalities or deletion of X chromosomes.
- Genetic disorders including autosomal disorders, such as galactosaemia (accumulation of galactose in the body due to the absence of an enzyme that metabolises galactose) and gonadotropin receptor dysfunction (dysfunction of the receptors of sex hormones) among others.
- Presence of environmental toxins or even smoking results in adverse effects on fertility.
How is it diagnosed and treated?
A general physician or a gynaecologist may suggest several diagnostic tests based on failed conception. Several tests suggested if suspicious of an ovarian failure are:
- Follicle stimulating hormone test (FSH) – In conditions of a premature ovarian insufficiency, the levels of FSH are quite high.
- Estradiol test – Found in the bloodstream, the levels of estradiol are very low in conditions of premature ovarian insufficiency.
- Karyotype - studying the chromosomes.
- FMR1 gene testing.
The main emphasis of the treatment is at the production or introduction of oestrogen in the body, which ultimately helps in relieving the symptoms like hot flashes and absent periods. Introduced along with progesterone, oestrogen helps in protecting the lining of the uterus, which becomes thin in this medical condition.

 OTC Medicines for Primary Ovarian Insufficiency
OTC Medicines for Primary Ovarian Insufficiency