What is a penile yeast infection?
Yeast is a type of fungus, which lives in different organs of the body like the digestive tract, mouth, on the skin, and genitals. Penile yeast infections occur when there is an overgrowth of the normally commensal yeast on the penis. This infection is also known as ‘candidiasis’, since an organism named ‘Candida albicans’ causes it. Candida infections are more prevalent in males with an uncircumcised penis than those with a circumcised one, as the moisture and warmth beneath the foreskin facilitate the growth of the yeast. Candida colonization is highly probable in men aged 40 years and above.
What are its main signs and symptoms?
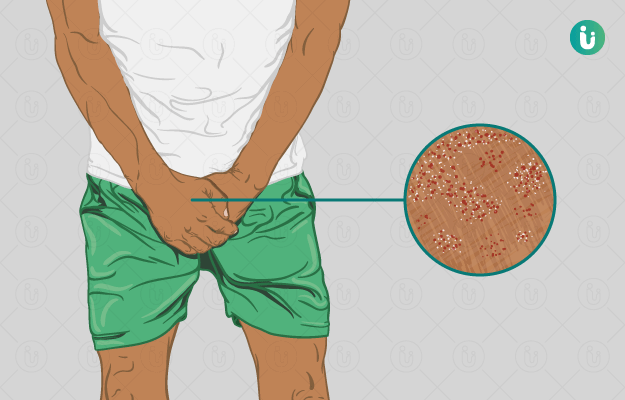
Penile yeast infection presents with the following symptoms on the underside of the penis:
- A painful rash.
- Scaling.
- Redness.
An itchy rash on the head of the penis is the most common symptom that men experience.
What are the main causes?
Following are the causes due to which yeasts overgrow leading to penile yeast infections:
- Humid or warm conditions.
- A weak immune system.
- Antibiotics (as they kill the healthy bacteria, which keep the growth of the yeast in check).
- People with certain diseases like HIV infection and diabetes are more susceptible to developing a yeast infection.
- Washing the penis with scented soaps and shower gels can irritate the skin and increase the risk of Candida multiplication.
- Unprotected sexual intercourse with a female who has a vaginal yeast infection.
How is it diagnosed and treated?
Your doctor will diagnose penile yeast infection by:
- Taking note of your medical history and symptoms.
- Performing a physical examination.
- Examining a scraping (a sample of fluid or tissue) of the penis.
Following are the available treatments for penile yeast infections:
- Anti-fungal creams or lotions.
- Medicated suppositories.
- Oral anti-fungal medications for individuals who contracted the infection due to weak immunity.
Most of these medications are available over-the-counter that can be taken without a prescription. If the infection persists even after using these medications, your doctor might advise a longer course of antifungals.

 Doctors for Penile Yeast Infection
Doctors for Penile Yeast Infection  Penile Yeast Infection articles
Penile Yeast Infection articles
 Home Remedies for Penile Yeast Infection
Home Remedies for Penile Yeast Infection






 Editorial Team
Editorial Team











