What is macular degeneration?
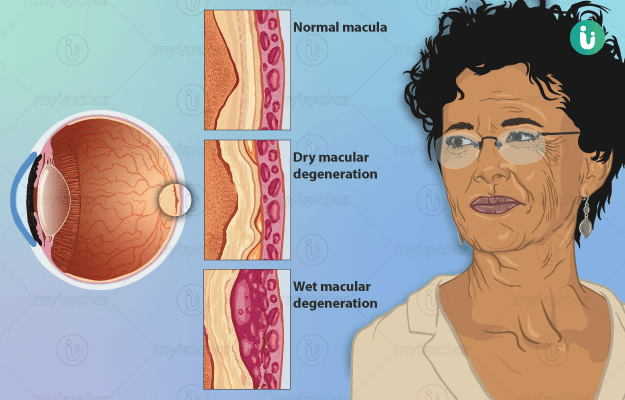
The macula of the eye is needed for sharp and central vision and appears near the centre of the retina as a small spot. The macula helps us locate objects straight ahead of us. Macular degeneration is a common eye condition caused by a damage to the macula. It can lead to vision loss in some people. Macular degeneration is of two types, dry and wet.
What are its main associated signs and symptoms?
Signs and symptoms of macular degeneration include:
- Red, painful eyes (Read more: Red eyes causes)
- Feeling as if a shadow or a dark curtain is present in the line of vision
- Straight lines appear to be crooked
- Blurred or distorted vision (Read more: Blurred vision treatment)
- Objects appearing smaller than normal
- Alterations in brightness of vision
- Hallucinations (seeing things that are not present)
- Struggle in looking at objects in the middle of your vision
- Loss of vision or fine vision loss
What are its main causes?
Macular degeneration is mainly caused by a damage to the retina leading to deterioration of the central portion of the retina. Causative factors of macular degeneration include:
- Heredity
- Environment
- Age
- Genetic, as seen in Stargardt disease
How is it diagnosed and treated?
Macular degeneration is diagnosed by an ophthalmologist who performs a thorough examination of the eyes with the following methods:
- Amsler grid: Examination of the eyes using a special lens while you look at an Amsler grid helps to locate changes in the retina and macula.
- Dilated eye examination: Eye drops may be used to dilate your eyes and widen your pupils for ease of viewing the retina during the examination.
- Visual acuity test using measurements from eye charts.
- Radiological techniques which include:
- Fluorescein angiography using fluorescein (yellow dye)
- Optical coherence tomography (OCT), which helps to scan the retina
Treatment of macular degeneration includes:
- Dry macular degeneration can be treated with minerals and vitamins such as
- Wet macular degeneration can be treated with:
- Photodynamic therapy, which includes giving the drug verteporfin intravenously
- Treatment with anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (anti-VEGF) drugs, which help in the reduction of the abnormal blood vessels in your retina
- Laser surgery

 Doctors for Macular Degeneration
Doctors for Macular Degeneration  OTC Medicines for Macular Degeneration
OTC Medicines for Macular Degeneration