What is Inflammatory Bowel Disease?
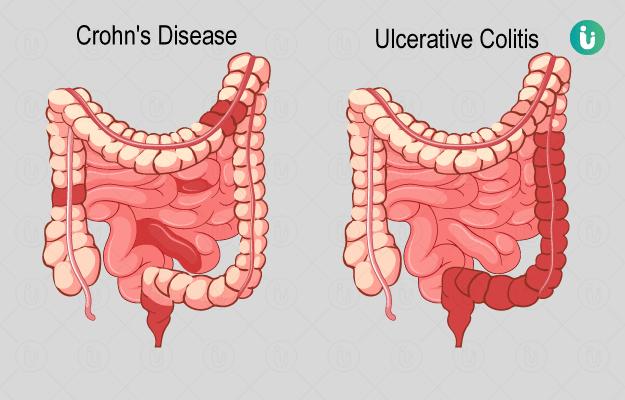
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a chronic disorder of the digestive or gastrointestinal (GI) tract marked by phases of inflammation or swelling and remission lifelong. Inflammation for prolonged periods leads to GI tract damage. Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis are the two types of inflammation patterns that occur under IBD. The large intestine is primarily affected in ulcerative colitis but any part of the GI tract from the mouth to the anus may get affected in Crohn’s disease.
What are the main signs and symptoms?
Mostly, people in the age group of 15 – 40 years are diagnosed with IBD. The symptoms may vary among people. A few of the symptoms are mentioned below:
- Pain or cramps in the stomach.
- Weight loss.
- Fatigue.
- Recurrent diarrhoea with or without blood or pus.
- Severe urgency for bowel emptying.
- Fever during the active phase of the disease.
Although IBD is persistent, the symptoms usually come and go depending upon the extent of inflammation. When the inflammation is severe, the disease is in the active stage, and when the inflammation subsides, the disease is considered to be in remission with mild symptoms.
What are the main causes?
The real cause of IBD is unknown, but the following factors are believed to be the reason for developing IBD.
- Genetic
You are more likely to suffer from this disease if you have a positive family history of IBD. - Weakened Immune System
Usually, your body attacks the foreign organisms, such as viruses or bacteria. When the immune system reacts against the body tissues, especially those of the gut, in response to environmental or other triggers, it leads to the inflammation of the GI tract.
How is it diagnosed and treated?
Beyond a physical examination and detailed history taking, IBD is usually diagnosed with a combination of endoscopy or colonoscopy and imaging studies, including MRI, CT scan, and contrast radiography. Stool examination and blood tests are done to confirm the diagnosis.
The main aim of the treatment is to reduce the inflammation of the gut and provide relief from the symptoms. Once under control, the medicines are continued to prevent relapse and maintain the remission period. This is called maintenance treatment. Surgery may be required in severe cases.

 Doctors for Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Doctors for Inflammatory Bowel Disease  OTC Medicines for Inflammatory Bowel Disease
OTC Medicines for Inflammatory Bowel Disease
 Inflammatory Bowel Disease articles
Inflammatory Bowel Disease articles News for Inflammatory Bowel Disease
News for Inflammatory Bowel Disease








 Dr. Nabi Darya Vali (AIIMS)
Dr. Nabi Darya Vali (AIIMS)











