A hernia is a condition in which any internal organ or any body part protrudes through the muscle wall or tissue wall. There are various types of hernia but the most common types of hernia are:
- Inguinal hernia: In an inguinal hernia, a portion of the intestines or some fat tissues poke into the groin that is at the top of the inner thigh.
- Femoral hernia: In a femoral hernia, a portion of intestines or some fat tissues bulge in the groin area at the top of the inner thigh.
- Umbilical hernia: In umbilical hernia, fat tissues are seen bulging out through the abdomen near the navel.
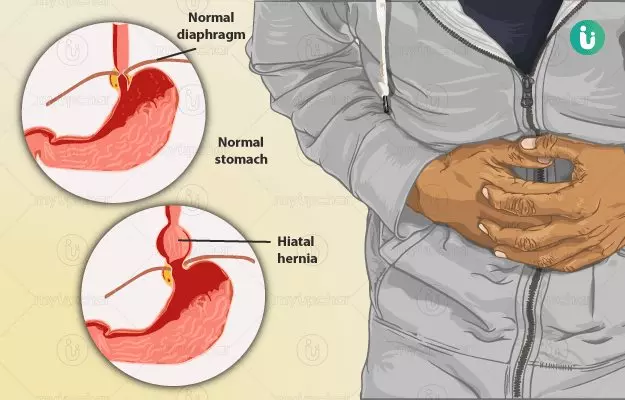
- Hiatal hernia: In hiatal hernia, a portion of the stomach pokes through the chest cavity right into the diaphragm.
There is a dome-shaped muscle called the diaphragm which acts as a barrier between the chest cavity and the abdominal cavity. There is a small opening in the diaphragm from where the food pipe (oesophagus) meets the stomach. Hiatal hernia is a condition in which the stomach pushes into the chest cavity from this opening in the diaphragm.
There is no certain cause for hiatal hernia but people aged 50 years and above are at higher risk of developing it. Obese people are also at risk of developing this disease. Women may also develop hiatal hernia during pregnancy due to excessive pressure on the diaphragm as the foetus grows bigger.
The treatment involves giving symptomatic relief using antacids, proton-pump inhibitors and anti-emetics (to stop the vomiting). People who do not respond to these medicines have to undergo surgery to correct the hernia and to prevent the reflux of acid (acidity) from the stomach to the food pipe (oesophagus).