Summary
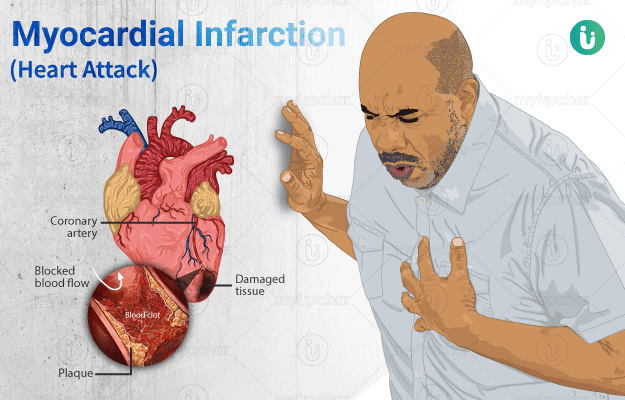
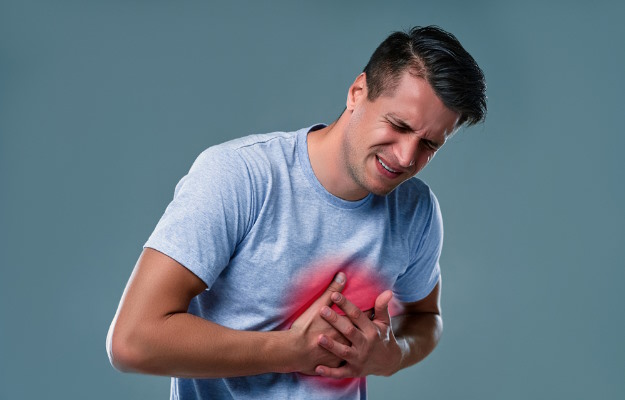
A heart attack is one of the most commonly witnessed medical emergencies, which can be fatal if not immediately attended to. It is a sudden event mainly caused by the obstruction of blood vessels supplying blood to the muscles of the heart. One of the most common reasons of heart attack is the fatty deposits called plaque in the walls of the arteries. A combination of smoking, unhealthy diet, obesity, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, alcohol, and a sedentary lifestyle increases the risk of heart attacks. An electrocardiogram (ECG) along with cardiac markers can help in the diagnosis of an acute heart attack. In the case of a massive heart attack, coronary angioplasty is also advised along with medications, and a bypass procedure is performed in occasional cases.
Click on the link to know in detail about heart disease treatment.
(Read More - First Aid for Heart Attack)

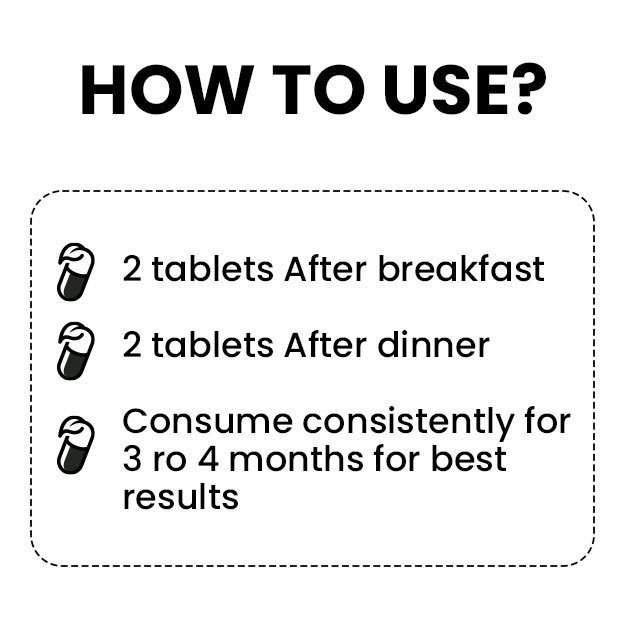
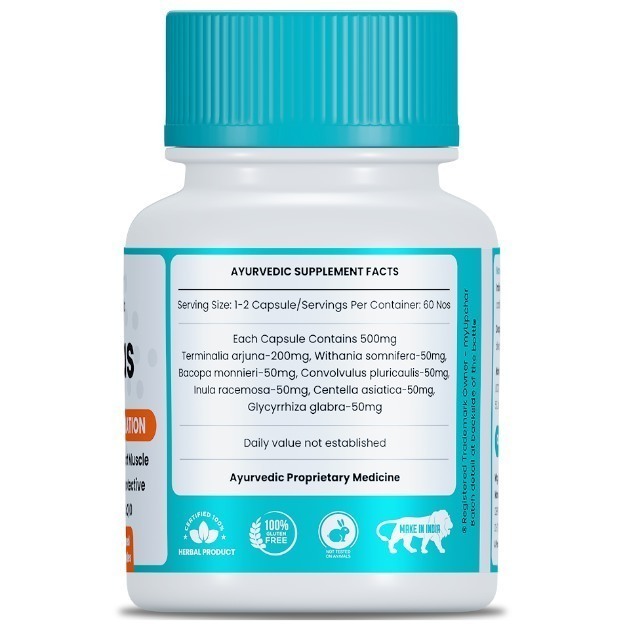
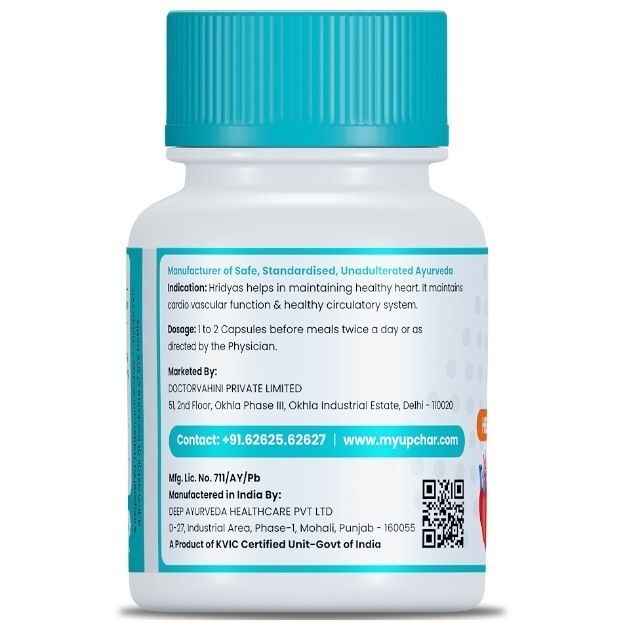
 OTC Medicines for Heart Attack
OTC Medicines for Heart Attack
 Lab tests for Heart Attack
Lab tests for Heart Attack Heart Attack articles
Heart Attack articles
 First Aid for Heart Attack
First Aid for Heart Attack
 Home Remedies for Heart Attack
Home Remedies for Heart Attack
 Homeopathic Treatment of Heart Attack
Homeopathic Treatment of Heart Attack










 Editorial Team
Editorial Team



 Dr. Laxmidutta Shukla
Dr. Laxmidutta Shukla













