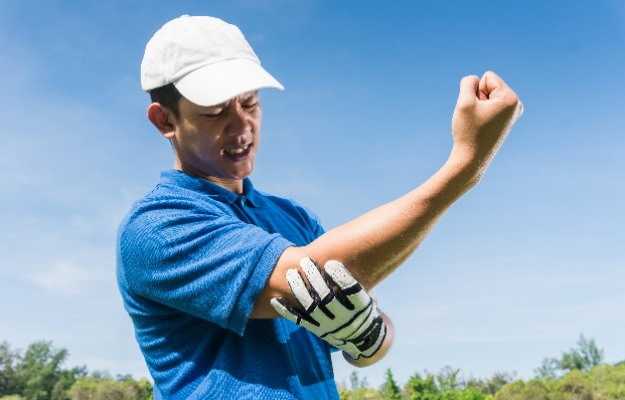
You don’t have to be a tennis player to suffer a tennis elbow - inflammation of the tendons that connect the muscles of the forearm to the outer part of the elbow joint. Similarly, you don't have to be a golfer to get golfer’s elbow.
Also known as medial epicondylitis, tendinosis, thrower's elbow and pitcher’s elbow, golfer's elbow causes pain and stiffness on the inside part of the elbow joint.
Golfer’s elbow occurs as a result of damage to the epicondyle - the bony bump on the inside of the elbow that attaches to the tendons and muscles in the forearms, wrists and fingers. Overuse of these muscles and tendons can result in the symptoms of golfer's elbow. This usually occurs in people who perform throwing actions or an exaggerated movement of the arm repeatedly.
While the pain of golfer's elbow can occur suddenly, injuries related to the tendons are usually caused by the repetitive movement of the same set of muscles, ligaments and tendons over a long time. It is usually not considered to be serious, as one can make a full recovery with proper rest and therapy.
To diagnose the condition, your doctor will perform a thorough physical examination and may also recommend an X-ray to rule out arthritis or fractured bone. The treatment protocol involves resting the area, wearing elbow support and eventually strengthening it through physiotherapy. In rare cases, surgery may be recommended for people who don't recover even after six months to a year.
Read more: Repetitive strain injury (RSI)

 Doctors for Golfer’s Elbow (Medial Epicondylitis)
Doctors for Golfer’s Elbow (Medial Epicondylitis)  OTC Medicines for Golfer’s Elbow (Medial Epicondylitis)
OTC Medicines for Golfer’s Elbow (Medial Epicondylitis)