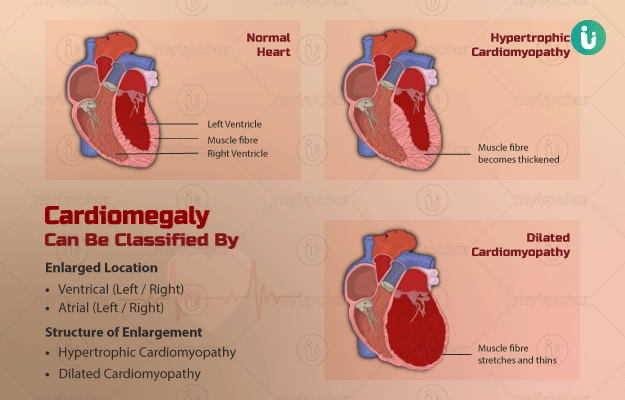
Also called cardiomegaly, an enlarged heart is not a disease by itself but an indication of a disease. It has several potential causes and may be temporary or permanent. This is usually diagnosed through an imaging test, after which other tests are undertaken to identify the condition causing enlargement of the heart. The condition is treatable using medication, medical procedures or surgery. However, some people with enlarged hearts require treatment throughout their life along with medication.
Here is the complete detail about coronary heart disease treatment.
(Read More - First Aid for Heart Attack)

 Doctors for Enlarged Heart
Doctors for Enlarged Heart  OTC Medicines for Enlarged Heart
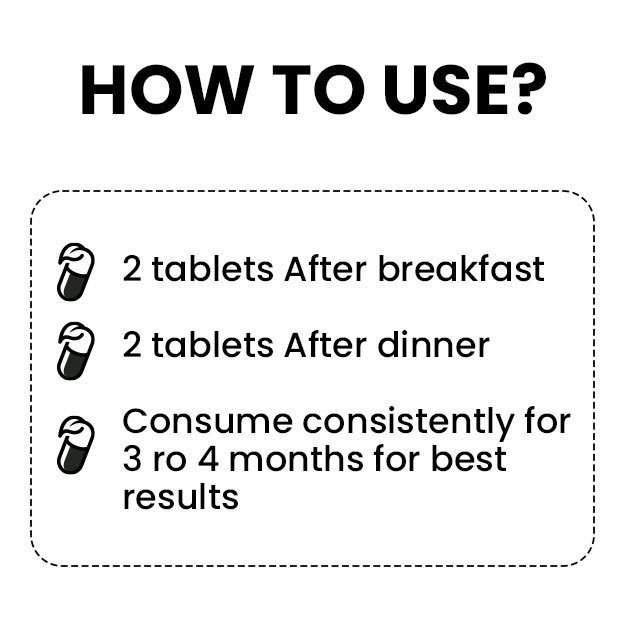
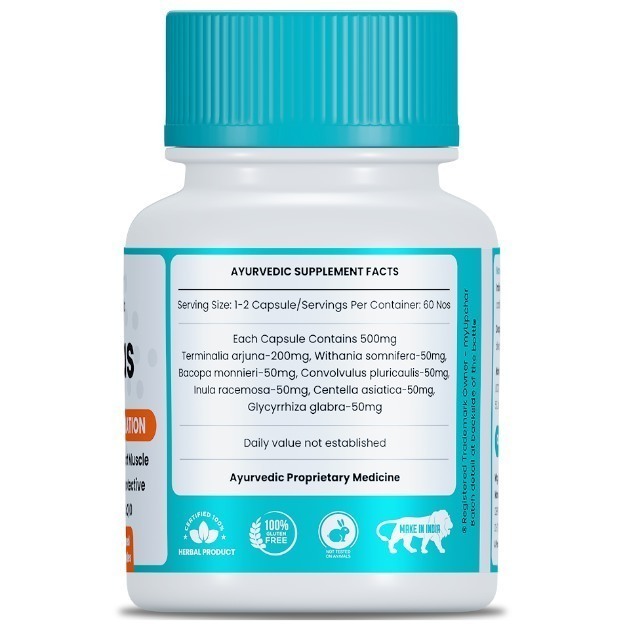
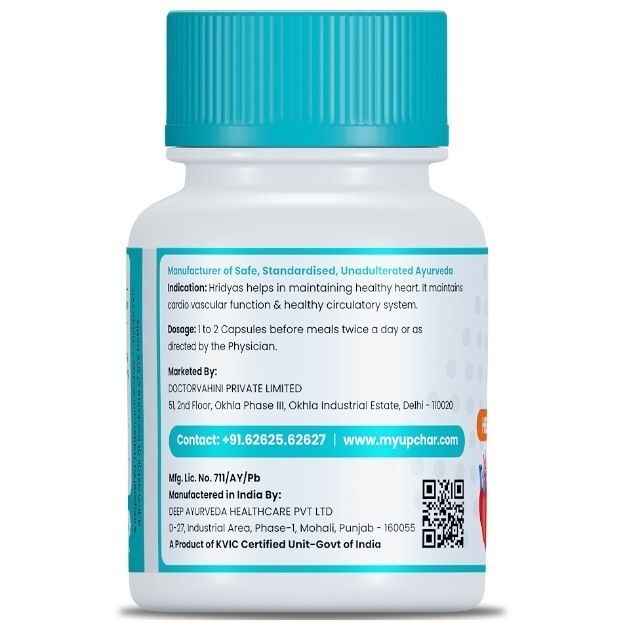
OTC Medicines for Enlarged Heart