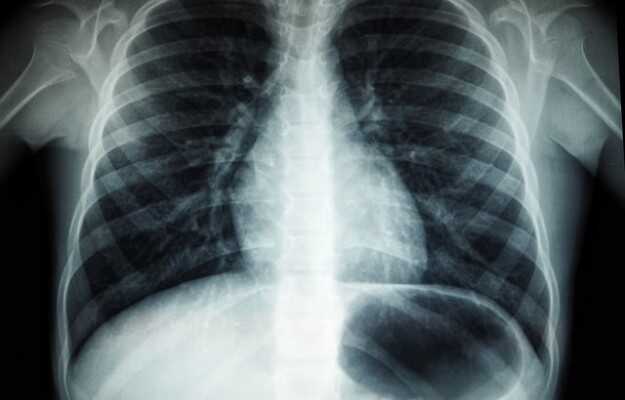
COVID-19, which first started spreading in December 2019 and was declared a pandemic in March 2020, is still spreading in 2021. While there are still many challenges to deal with today, there are also many learnings since the beginning of the pandemic that can be applied to better diagnose and treat the condition. The diagnosis of active infection is based on the results on an RT-PCR (real-time reverse-transcriptase polymerase chain reaction) test. Antibody tests are also used to the detection of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies in the patient’s blood. Additionally, a chest CT scan or a chest HRCT scan may be ordered as a diagnostic tool or to understand the progression of the disease through the damage caused to the lungs.
CO-RADS stands for COVID-19 Reporting and Data System and was specifically developed by Dutch researchers to better deal with COVID-19. It is a system that aims to standardize the assessment of pulmonary involvement in COVID-19 cases. It is not the only system of this kind, another one being the RSNA (Radiological Society of North America) chest CT classification system for reporting COVID-19 pneumonia. There are 7 CO-RADS categories from 0 to 6. The categorization is done based on non-enhanced CT scan results as well as symptom presentation when RT-PCR results are unavailable. CT scan results come in much faster than RT-PCR results, which can be life-saving in situations where the patient’s condition is serious and their COVID-19 status is not established.