Summary
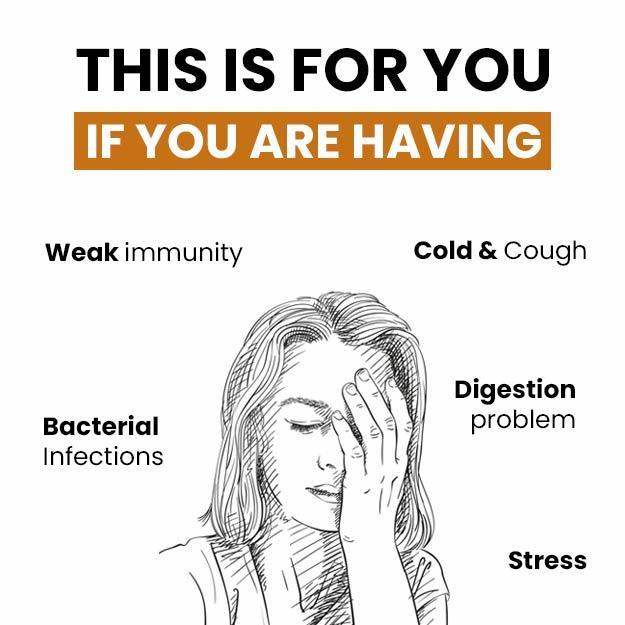
Coughing is an impulse that keeps your airways and throat clear of mucus and irritants like smoke or dust. A dry cough gives a tickly sensation in the throat with no production of phlegm (thick mucus) whereas, in a productive cough, there is phlegm production, which clears the airway. In most people, a cough clears up in less than three weeks without the need of any medications. However, when a cough is persistent, it is good to see your doctor for prompt treatment.
There are many medical conditions that could cause a persistent cough, for example, flu, sinusitis, laryngitis, allergic rhinitis or just a flare-up or an acute exacerbation of a chronic disease like asthma, chronic bronchitis or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Medications aren't always needed for a short-term cough because it gets better within a few weeks. Sufficient rest with adequate fluid intake and simple home remedies can help. If your cough is because of a specific reason, treating the underlying cause may help. In rare cases, a persistent cough can be a symptom of a severe health condition, for example, tuberculosis or cystic fibrosis, which must be managed timely. Let’s learn and explore more about this impulse through this article.

 Doctors for Cough
Doctors for Cough  OTC Medicines for Cough
OTC Medicines for Cough
 Cough articles
Cough articles

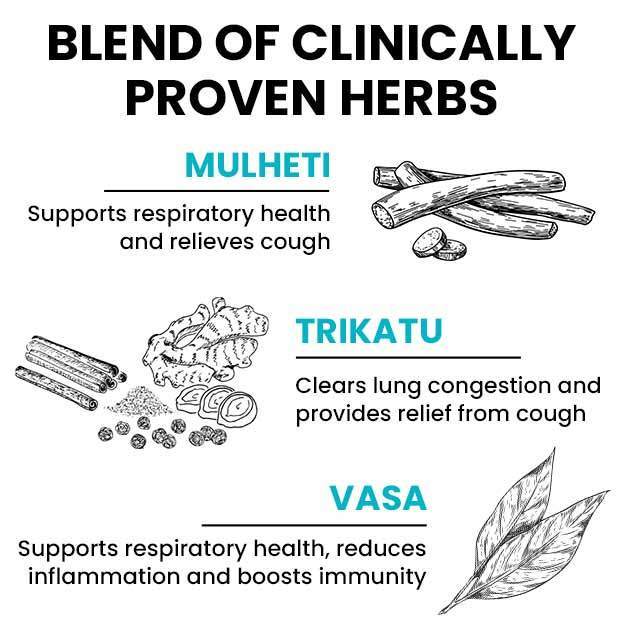
 Ayurvedic Treatment of Cough
Ayurvedic Treatment of Cough
 First Aid for Cough
First Aid for Cough
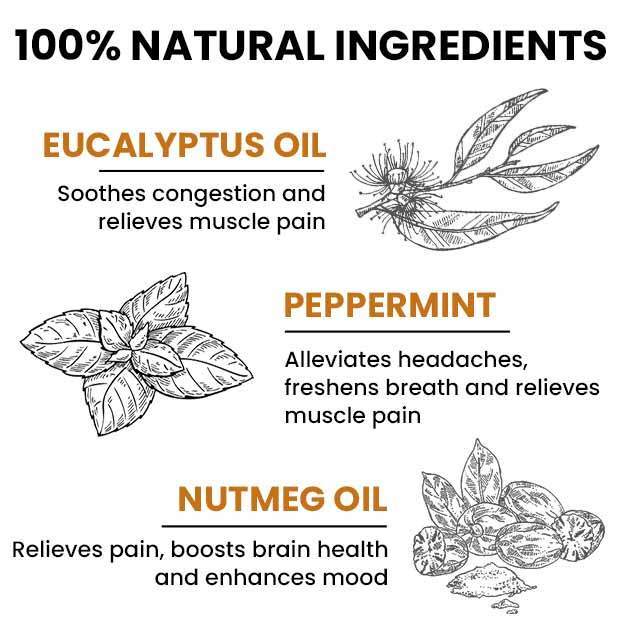
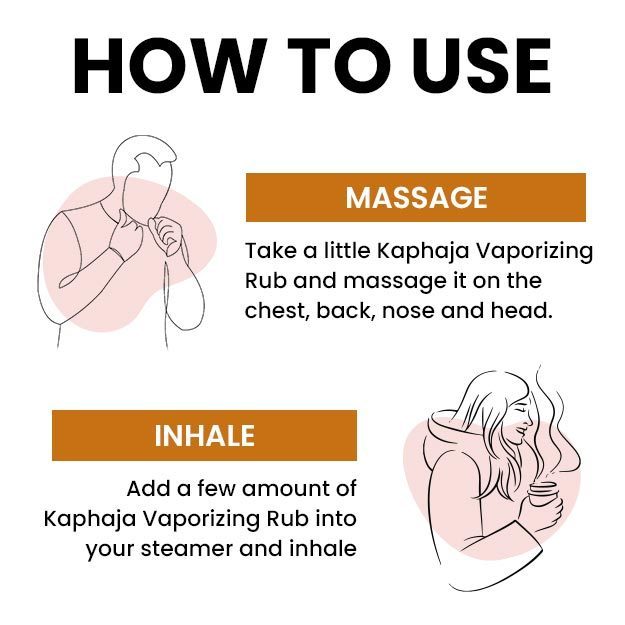
 Home Remedies for Cough
Home Remedies for Cough
 Homeopathic Treatment of Cough
Homeopathic Treatment of Cough























 Editorial Team
Editorial Team




 Dr. Laxmidutta Shukla
Dr. Laxmidutta Shukla











