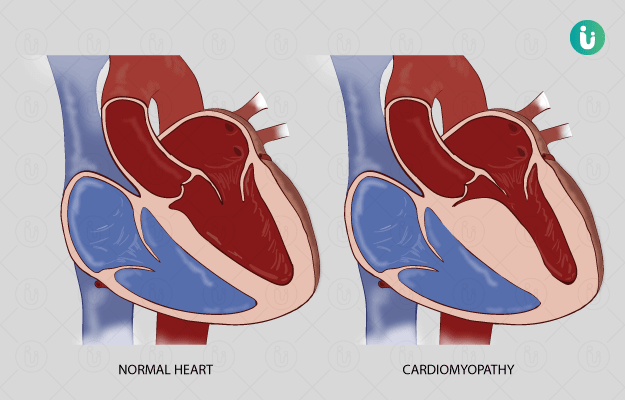
What is cardiomyopathy?
Cardiomyopathy is a condition of the heart muscles due to which pumping of blood to the rest of the body becomes more difficult. While those who have cardiomyopathy can lead normal lives with proper care and attention, it can, in some cases lead to heart failure. Care for cardiomyopathy depends on the type of the problem suffered – dilated, hypertrophic or restricted.
Here is the complete detail about heart disease treatment.
(Read More - Homeopathic treatment for heart attack)
What are its main signs and symptoms?
In the early stages it might be hard to notice any signs, but eventually, some symptoms appear. These include:
- Swelling around ankles and feet
- Fatigue, even without apparent exertion
- Bloating of the stomach persistently
- Palpitation or pounding heartbeat
- Constriction of the chest
- Giddiness or feeling light-headed
- Breathlessness
(Read More - Heart valve replacement)
What are its main causes?
The main cause of the condition is hard to ascertain, while in some cases it may be hereditary. Factors that could contribute are:
- Blood pressure related ailments
- Damage from heart attack
- Heart rate problems and problems with the valves (arrhythmias and valve defects)
- Abuse of alcohol and drugs
- Heart infections (endocarditis)
- Inflammation in the heart (pericarditis)
- Protein deposits
- Tissue disorders
- Chemotherapy
- Complications in pregnancy
- Nutritional deficiency
- Disorders like diabetes, thyroid and obesity
(Read More - Pacemaker Surgery)
How is it diagnosed and treated?
The primary diagnosis involves a physical examination along with screeners for family history and record of previous ailments. After ascertaining the causes, doctors may suggest:
- X-Ray
- ECG to check beating of heart and valves
- Stress test on the treadmill to check symptoms
- Catheterization to check blood vessels
- Blood test for function of all organs
- Genetic testing
Treatment depends on the nature of cardiomyopathy.
- Medication may be given to lower blood pressure, increase blood flow, slow heart rate and prevent clot formation
Implanted devices:
- ICD or implantable cardioverter defibrillator to assess the heart rhythm
- VAD or ventricular assist device to help blood circulation
- Pacemaker to control arrhythmia
- Ablation to thin the heart wall and ease blood flow, or to reduce damaged portions which cause arrhythmia
- Surgical procedures like open heart surgery to remove some heart muscle and improve blood flow, or in extreme cases, heart transplants
- Lifestyle changes like losing weight, exercise, improved diets, quitting smoking and alcohol consumption, and managing stress and sleep
(Read More - Aortic valve repair)

 Doctors for Cardiomyopathy
Doctors for Cardiomyopathy  OTC Medicines for Cardiomyopathy
OTC Medicines for Cardiomyopathy
 Cardiomyopathy articles
Cardiomyopathy articles
 Diet for Cardiomyopathy
Diet for Cardiomyopathy
 Home Remedies for Cardiomyopathy
Home Remedies for Cardiomyopathy







 Dr. Laxmidutta Shukla
Dr. Laxmidutta Shukla

 Dr. Ayush Pandey
Dr. Ayush Pandey











