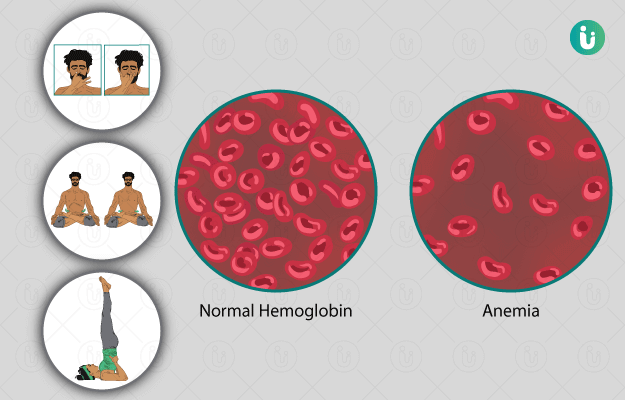
The blood in our body is the only medium through which oxygen travels in the body. Our blood contains red blood cells which in turn contain haemoglobin - an iron-rich protein that sticks to the oxygen molecules in the lungs and then transfers it to the blood capillaries which travel throughout the body.
Anaemia is a condition in which the quality or the number of red blood cells in the body reduces. A person with anaemia does not have enough oxygen-rich blood. This leads to various symptoms like:
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
- Dizziness
- Headaches
- Arrhythmia (irregular heartbeat)
Mild anaemia is a common condition mostly seen in women, especially during menses and pregnancy. It can be managed easily with the help of iron-rich food and iron supplements. Sometimes, anaemia can also be a sign of many underlying serious conditions such as bleeding ulceration in the stomach, kidney disease or an autoimmune disease like autoimmune hemolytic anaemia.
Often, people get anaemic due to lack of iron in the body - this is known as iron-deficiency anaemia. The body needs iron to make red blood cells and haemoglobin which are essential for delivering oxygen to various organs of the body.
In order to fulfil the need for iron in the body, dietary changes should be made and food rich in iron, protein, folate (vitamin B9) and vitamin B12 should be included in the diet.
There are basically two types of iron that are derived from food sources: heme iron and nonheme iron. Heme iron is derived from meat, poultry and seafood. And non-heme iron is derived from plant sources. Heme iron is more easily and well absorbed by the body.