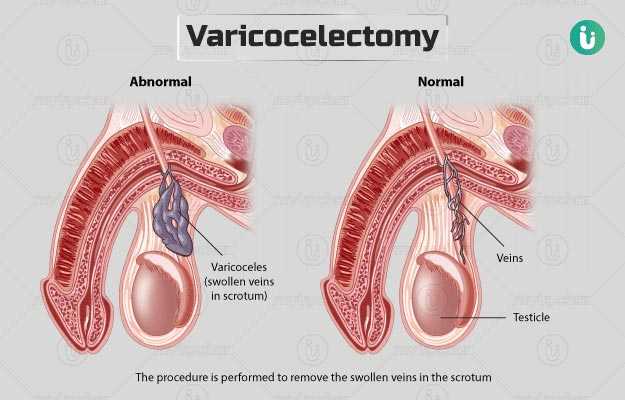
The duration of varicocelectomy is about two to three hours. The following steps are carried out during the surgery:
- You will be given general anaesthesia that will make you sleep during the procedure.
- However, if spinal anaesthesia is considered, you will receive an injection in your lower back that will make your lower body feel numb. If local anaesthesia is considered, you will receive an injection in the specific area that will be operated.
- An intravenous line, which will supply fluids and medicines, will be put into a vein in your arm.
- You might be given a medicine to prevent blood clots.
- A tube will be inserted into your throat to assist in breathing.
- A catheter (thin tube) will be put in your bladder to drain urine.
Laparoscopic varicocelectomy
During a laparoscopic varicocelectomy, the surgeon will make a few small cuts on your abdomen. A laparoscope (a thin, lighted tube) will be placed through one of the incisions, and the abdomen will be filled with gas to allow the doctor to see clearly the inside of your body. With the help of the other tools inserted through the other openings, the doctor will cut the swollen veins and seal their ends with tiny clips. All the tools will be removed once the operation is complete, and the incision will be closed with stitches.
Open surgery
If you undergo an open surgery technique is used, the doctor will make an incision will be made on your abdomen or the groin and he/she will cut and seal the swollen veins through this incision. A microscope is sometimes used during an open varicocelectomy. The magnification due to the microscope helps the surgeon identify and work on the tiny veins and preserve the small arteries and vessels carrying fluid around the testicles.
After the surgery, you will be taken to a recovery room to monitor your vitals for one or two hours before shifting you to a normal ward.
When you wake up, you will feel drowsy for a while due to the anaesthesia, and your throat might be sore if a breathing tube has been used. When you can get up on your own, the catheter from your bladder will be removed. Your doctor will give you some medicines to manage the pain.