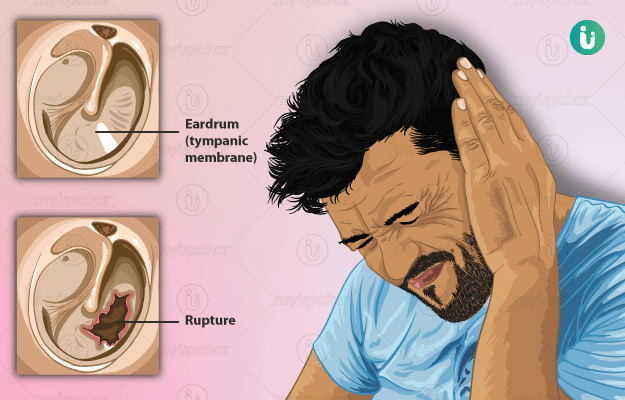
Tympanoplasty is a surgical procedure that is done to repair a perforated eardrum using a piece of tissue. The surgery is employed in large perforations which cannot heal by themselves.
Investigations prior to tympanoplasty include blood tests, radiological tests and special hearing tests. The surgery is done under general anaesthesia and requires a few days of hospital stay.
Aftercare post-surgery is important to ensure proper healing and thereby restore the function of the ear.