Summary
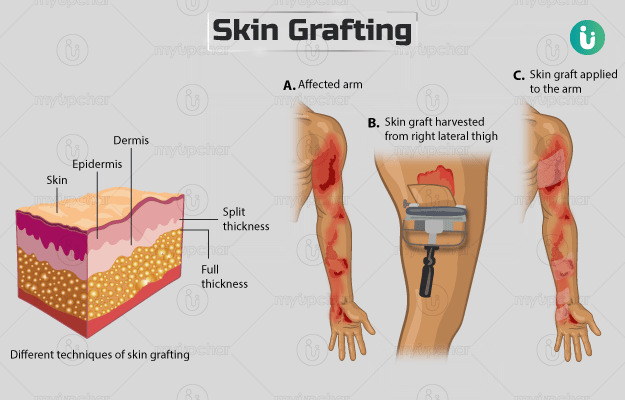
Skin grafting is a surgical technique in which damaged or missing skin in an area is replaced with healthy skin, usually for the treatment of conditions like burns or skin cancer. The new skin that acts as a replacement (graft) may come from your own body or other sources. However, you may not be eligible for the surgery if you have any active infection or conditions that may cause complications. Certain tests will be needed to determine your eligibility for surgery, and you must share your entire medical history with the surgeon. There are different techniques to obtain the graft depending on the requirement and the surgery is usually completed in about one to three hours. Care after surgery will strictly involve the two incision sites, the donor site and the receiving site. You should not perform strenuous exercises or lift heavy weights while the graft heals. The surgery has a few risks such as excessive bleeding, infection or swelling at the donor or recipient sites. Your follow-up visit will be one week after the surgery, but you must rush to the healthcare expert if you observe any symptoms such as fever, nausea or vomiting.