Summary
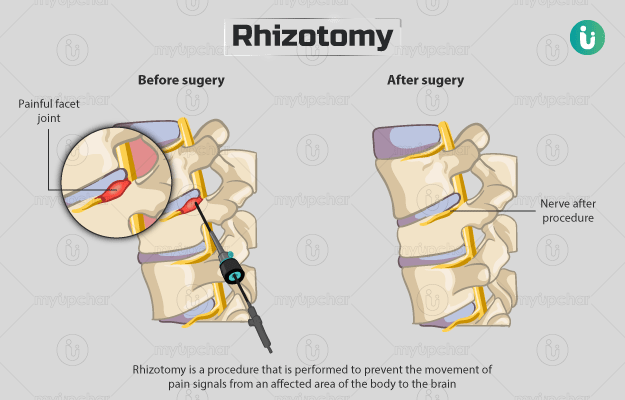
Rhizotomy is a surgical procedure to cut nerve roots from the spinal nerves and restrict pain signals from an affected area in the body from reaching the brain. This action is usually performed on the facet joint, which is located at the back of the spinal bones. Before the surgery, the surgeon will examine your health thoroughly via a few diagnostic tests. You will be asked about your current and previous medications and illnesses during the evaluation. The surgery will be conducted under local anaesthesia, which will only numb the surgical area. After the surgery, you will need to take proper care of the surgical area for a faster and healthier recovery.